Celanese AMCEL KP30 Hot Sale POM Resin

Celanese Amcel KP30 Summary
Celanese Amcel KP30 is a polyoxymethylene (POM) copolymer produced by Celanese Corporation. Amcel KP30 is an engineering thermoplastic supplied in pellet form, specifically designed for the injection molding process. Its core defining characteristic is its low viscosity and high flowability, quantified by a Melt Mass-Flow Rate (MFR) as high as 27 g/10 min (at 190℃/2.16kg).
This high flowability constitutes the primary value proposition of Amcel KP30: it significantly enhances processing performance, making it an ideal choice for manufacturing precision components with complex geometries, thin walls, or long flow paths. Furthermore, its ability to fill and solidify rapidly contributes to shorter molding cycles, yielding substantial economic benefits in large-scale production. Beyond its exceptional processability, Amcel KP30 exhibits the balanced performance profile typical of acetal copolymers, including high stiffness, excellent dimensional stability, and natural lubricity (low coefficient of friction). These attributes make it a general-purpose grade widely used in sectors such as automotive, industrial machinery, and consumer electronics for components like precision gears, bearings, fasteners, and connectors.
However, the selection of Amcel KP30 necessitates acknowledging a fundamental engineering trade-off: the enhancement of processing performance comes at the cost of some ultimate mechanical toughness. A basic principle of polymer science dictates that a material’s melt flow rate is inversely proportional to its average molecular weight. The high MFR of Amcel KP30 implies a relatively lower average molecular weight. A lower molecular weight typically results in reduced polymer chain entanglement, which in turn diminishes certain mechanical properties, particularly those related to toughness, such as impact strength and elongation at break. This is clearly illustrated by a direct comparison with Amcel KP20 from the same series (MFR of 9 g/10 min): KP20 has a higher Charpy notched impact strength (5.8−6.5 kJ/m2), whereas KP30 value is 5.0−6.0 kJ/m2. Therefore, for an engineer, choosing KP30 over a medium-flow grade like KP20 is a clear strategic decision to prioritize molding convenience (for complex parts or fast cycles) over achieving the material’s maximum possible impact resistance. This report will revolve around this core trade-off to provide comprehensive data and analysis for material selection, part design, and process optimization.
Amcel KP30 Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Performance Indicator | Value |
Material Type | Polyoxymethylene (POM) Copolymer |
Defining Feature | High Flow / Low Viscosity |
Melt Mass-Flow Rate (MFR) (190℃/2.16kg) | 27 g/10 min |
Tensile Modulus | Approx. 2700 MPa |
Tensile Stress at Yield | 65 MPa |
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) @ 1.8 MPa | 95℃ |
Primary Processing Method | Injection Molding |
Material Characteristics & Technical Specifications
This section aims to provide an authoritative technical reference for Amcel KP30, consolidating and calibrating performance parameters from multiple data sources to offer a solid foundation for engineering design and analysis.
Product Identification & Procurement Information
- Manufacturer: Celanese Corporation, a leading global supplier of engineering materials.
- Product Family & Grade: Amcel KP30. Amcel is a registered trademark of Celanese.
- Chemical Family: Polyoxymethylene (POM), specifically an Acetal Copolymer.
- Physical Form: Supplied as Pellets.
- Commercial Status: Commercially available grade, accessible in North America and other global regions.
- Suppliers/Distributors: Available for purchase through Sales Plastics and other channels.
Comprehensive Performance Overview
To provide engineers with a single, reliable data source, the following table consolidates information from multiple Technical Data Sheets (TDS) and unifies all values into metric (SI) units. This helps to mitigate potential design risks arising from inconsistent data sources or unconverted units.
Amcel KP30 Consolidated Technical Data Sheet
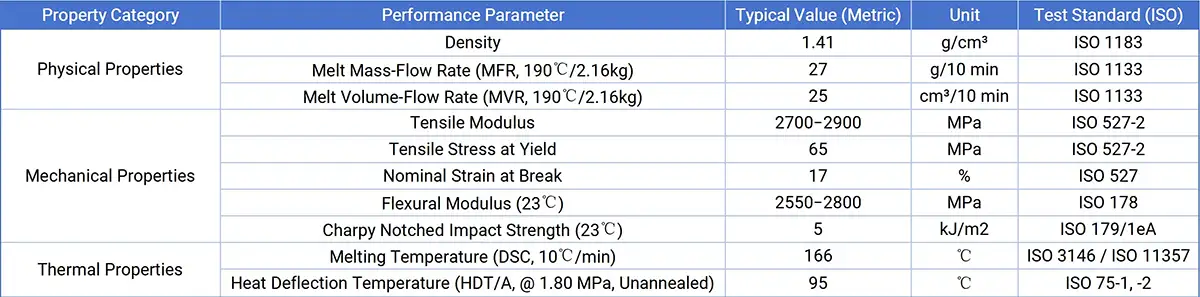
Data Sources: Note: Some values (e.g., modulus) were converted from imperial units (psi) and consolidated from multiple sources, hence presented as a range.
Key Performance Analysis & Design Implications
Rheological Properties (Flow Behavior)
The MFR of Amcel KP30 is 27 g/10 min (ISO 1133), which is its most significant material characteristic. This value clearly classifies it as a “high-flow” or “low-viscosity” grade.
- Design Impact: This exceptional flowability provides tremendous flexibility in product design. It facilitates the filling of mold cavities with long flow paths, thin walls (down to 0.5 mm), and intricate details. On a manufacturing level, this means lower injection pressures can be used, reducing equipment requirements and potentially shortening molding cycles significantly, thereby lowering unit production costs and improving overall manufacturing efficiency.
Mechanical Properties
- Stiffness & Strength: With a Tensile Modulus of approximately 2700−2900 MPa and a Flexural Modulus of about 2550−2800 MPa, Amcel KP30 is a highly rigid material. It is well-suited for load-bearing applications requiring minimal deformation, such as structural brackets, housings, and gears.
- Toughness: Its Charpy notched impact strength is approximately 5.0 kJ/㎡ , which is a moderate value among engineering plastics.
- Design Impact: This is a critical limitation for designers to consider when using KP30. The material is not suitable for parts that must withstand high-energy, sudden impacts or require high ductility. Its high flowability is achieved at the expense of some toughness. For safety-critical components or parts susceptible to impact, a careful impact performance evaluation should be conducted, or tougher, medium-to-low flow grades should be considered.
Thermal Properties
- Multiple data sources consistently report a melting point of 166 ℃ (measured via DSC).
- The Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) under a 1.8 MPa load is 95 ℃. Although one source indicates it could be as high as 106 ℃ , for conservative design, the lower value of 95 ℃ should be used as the reference benchmark.
- Design Impact: This HDT value defines the upper limit for continuous use temperature under moderate load. This means KP30 can maintain its structural integrity and dimensional stability in environments up to approximately 95 ℃. For applications requiring operation above this temperature, higher-performance engineering plastics must be selected.
Processing & Manufacturing Guide

This section aims to provide a practical, actionable guide for plastics processors, emphasizing best practices, key process parameters, and critical safety protocols for Amcel KP30. This guide primarily references the detailed processing manual provided by Celanese for its similar Celcon product , combined with specific parameters from KP30 own technical data sheets.
Recommended Injection Molding Parameters
To help process engineers quickly set up and optimize production, the following table summarizes the recommended injection molding parameters for Amcel KP30.
Recommended Injection Molding Process Settings for Amcel KP30
Parameter | Recommended Value (Metric) | Recommended Value (Imperial) | Notes |
Melt Temperature | 185−195℃ | 365−383℉ | Preferred range; avoid exceeding 238℃. |
Mold Temperature | 80−90℃ | 176−194℉ | High mold temperature helps achieve better surface finish and dimensional stability. |
Drying (if required) | 3−4 hours at 82℃ | 3−4 hours at 180℉ | Only needed if material is exposed to moisture; dehumidifying dryer recommended. |
Back Pressure | Low | Low | Low back pressure is recommended to minimize shear heat and prevent material degradation. |
Injection Speed | Medium to High | Medium to High | Due to low viscosity, higher speeds can be used, but optimize to prevent jetting. |
Material Handling & Preparation
- Storage: Amcel KP30 should be stored in its original, sealed packaging in a dry environment to prevent moisture adsorption on the pellet surface.
- Drying: Acetal copolymers have very low moisture absorption and can typically be processed directly without drying. However, if the material has been exposed to humid air for extended periods, or to ensure the highest level of process consistency, pre-drying is considered good manufacturing practice. Processing undried, moist material can lead to splay marks on the part surface and a pungent odor.
Contamination Prevention: It is strongly recommended to install magnetic separators at the hopper feed throat to capture any metallic impurities that may have been introduced during transport and handling, thereby protecting the screw and mold from damage.
Key Processing & Safety Considerations
When processing Amcel KP30, two areas require the highest level of attention: chemical incompatibility with specific materials and the risk of thermal degradation. These concern not only product quality but also directly relate to operator safety and equipment integrity.
Severe Incompatibility with Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Processing guides explicitly and sternly warn: Acetal copolymers (like Amcel) must never be mixed with polyvinyl chloride (PVC), not even in trace amounts. The importance of this point far exceeds that of ordinary material contamination. When these two materials come into contact in a molten state, the thermal decomposition products of PVC (primarily acidic substances) act as powerful catalysts, triggering a violent, rapid chain-scission reaction in the acetal polymer. This is not a simple physical mixing but a potentially uncontrollable chemical reaction.
This reaction releases large quantities of formaldehyde gas and can generate extremely high pressure within the barrel, posing a risk of equipment (e.g., nozzle, screw) rupture or melt blow-back through the hopper, which is a severe hazard to personnel and equipment. Therefore, if a facility processes both POM and PVC, extremely strict segregation and cleaning procedures must be established. When changing materials, simply “purging” with a general-purpose plastic may be insufficient. In cases of known or suspected contamination, the official recommendation is to completely dismantle and thoroughly mechanically clean the processing equipment (including the barrel, screw, check ring, screw tip, and nozzle). The cost of this operation (including downtime and labor) is substantial, making this risk a critical strategic consideration in production planning and shop floor management.- Thermal Degradation & Formaldehyde Release: When processed outside the recommended temperature range (above 238℃) or with excessive residence time in the barrel (e.g., more than 15 minutes above 193℃), Amcel KP30 will undergo thermal degradation. The primary byproduct of this degradation is formaldehyde gas. Formaldehyde is a colorless, pungent gas that is harmful to humans in high concentrations.
Therefore, ensuring good ventilation in the processing area is crucial, and installing a local exhaust hood over the injection molding machine’s barrel unit is strongly recommended. This is not just a best practice but a fundamental requirement for protecting operator health and safety. The latest Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) must be consulted and understood before attempting to process any Amcel product.
Regrind Use & Secondary Operations
Regrind Use: In most applications, up to 25% regrind can be incorporated. The regrind must be clean, dry, and free of any contamination. Since regrind pellets have a larger surface area, their tendency to absorb moisture may be greater than virgin material, making thorough drying before use particularly important.
- Secondary Operations: Molded parts from Amcel KP30 have excellent machinability. They can be cut, drilled, punched, polished, and tapped using standard tools and methods designed for soft metals like brass and aluminum. Additionally, it is suitable for surface decoration processes such as hot stamping, pad printing, and laser marking.
Application Analysis & Performance Context

This section aims to connect the technical characteristics of Amcel KP30 with its real-world applications, helping designers and engineers understand where it can deliver maximum value and what its performance boundaries are.
Primary & Potential Applications
The core advantages of Amcel KP30 lie in its unique combination of high flowability, high stiffness, and low coefficient of friction. This set of properties makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing small, structurally complex, high-precision mechanical transmission and structural components.
Industry-Specific Application Examples :
Automotive Industry: Due to its good chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and mechanical strength, KP30 is widely used in fuel system components (e.g., fuel pump modules, floats, valves), precision gears, bearings, door lock system components, and various fasteners.
Industrial & Consumer Goods: In industrial equipment and home appliances, KP30 is often used for sliding elements, hinges, electrical connectors, and internal mechanical parts of printers and copiers. Its natural lubricity is particularly important in these applications requiring low-friction movement.
Medical Sector: Amcel POM can be used for certain medical device housings or non-implantable components. However, it must be emphasized that all data sheets explicitly state that this material must not be used for medical or dental implants. This is an absolute design prohibition.
Case Study: High-Flow POM in Automotive Fuel Systems
Modern automotive fuel systems place stringent demands on materials: they must be lightweight to improve fuel economy, resistant to the chemical attack of increasingly complex fuel blends, and capable of being molded into intricate shapes to fit compact engine compartments and enable parts integration.
Role of Amcel KP30 in this Scenario:
Realization of Complex Geometries: Components like fuel pump modules, fuel sending units, and multi-way valve bodies have extremely complex internal structures. The high flowability of Amcel KP30 ensures that the molten plastic can completely fill these minute details and thin-walled sections, enabling the design of integrated parts that combine multiple individual components into a single injection-molded piece. This not only reduces weight but also decreases assembly steps and potential leak points.
- Dimensional Stability & Sealing: Acetal copolymers have extremely low moisture absorption, meaning their dimensions change very little in humid environments or when in contact with liquid fuels. Combined with its high stiffness, this ensures that critical dimensions in the fuel system (such as sealing flanges and valve seats) remain stable throughout the vehicle’s lifecycle, thus ensuring system integrity and performance reliability.
- Chemical Resistance: As a copolymer, Amcel KP30 has good resistance to hydrocarbons, alcohol-based fuels, and other automotive chemicals, allowing it to maintain its performance stability over long periods in a fuel environment.
Comparative Analysis & Market Positioning

To provide decision-makers with crucial context, this section benchmarks Amcel KP30 against its most direct internal and external competitors and analyzes its position within the broader engineering plastics market.
Intra-Series Comparison: The Trade-off Between Flowability and Toughness
Within Celanese’s Amcel product line, KP30 and KP20 are two adjacent grades that perfectly illustrate the classic “flowability-toughness” trade-off in polymer engineering. The choice between them directly reflects an application’s priority ranking of processability versus mechanical performance.
Amcel KP30 (High Flow) vs. Amcel KP20 (Medium Flow) Comparison
Performance Parameter | Amcel KP30 (High Flow) | Amcel KP20 (Medium Flow) | Analysis & Trade-off |
MFR (g/10 min) | 27 | 9 | KP30 flowability is three times that of KP20, greatly simplifying the molding of complex parts. |
Tensile Modulus (MPa) | 2700−2900 | 2600−2850 | Stiffness is very similar; the difference is often not significant in engineering applications. |
Nominal Strain at Break (%) | 17 | 30 | KP20’s ductility is significantly better, meaning it can withstand greater deformation before fracture. |
Charpy Notched Impact Strength (kJ/m²) | 5.0 | 5.8 – 6.5 | KP20’s impact toughness is approximately 16% to 30% higher than KP30, a significant performance advantage. |
The conclusion from the table is clear: when an application has higher requirements for impact resistance and the part geometry is relatively simple, Amcel KP20 is the more robust choice. Conversely, when the core design challenge is to achieve complex, thin-walled structures, or when production efficiency (i.e., molding cycle time) is a key cost driver, the high flowability of Amcel KP30 offers an irreplaceable advantage.
Copolymer vs. Homopolymer: The Trade-off Between Stability and Strength
The polyoxymethylene (POM) market is primarily divided into two categories: copolymers (POM-C, like Amcel) and homopolymers (POM-H, like DuPont™ Delrin). The differences in their molecular structures lead to different performance emphases, and the choice depends on the application environment and primary performance requirements.
Acetal Copolymer (POM-C) vs. Acetal Homopolymer (POM-H) Performance Comparison
Performance Dimension | Acetal Copolymer (e.g., Amcel) | Acetal Homopolymer (e.g., Delrin) | Selection Consideration |
Chemical & Thermal Stability | Superior. Better resistance to hot water, alkaline environments, and thermal-oxidative degradation. | Good, but relatively weaker. Not resistant to strong acids, bases, or oxidizing agents. | If the part must work long-term in humid, hot water, or chemical environments, copolymer is the preferred choice. |
Processing Window | Wider. Less sensitive to temperature variations and less prone to degradation during processing. | Narrower. Must be processed within a very precise temperature range to prevent degradation. | Copolymers offer processors greater flexibility and a larger margin for error. |
Mechanical Properties (Short-term) | Good. | Superior. Higher tensile strength, stiffness, hardness, and creep resistance. | If the primary challenge is to withstand high static or cyclic loads, homopolymers have a performance advantage. |
Centerline Porosity | Less prone. Extruded profiles have more uniform core density. | More prone. Due to rapid crystallization, the core of profiles is susceptible to microporosity. | For thick-walled parts or those requiring high internal density, copolymers perform better. |
Competitive Landscape: A General-Purpose Product in a Crowded Field
A deeper market analysis reveals that Amcel KP30 is not a unique specialty material but rather Celanese’s strong contender in the high-flow, standard-grade POM copolymer segment. Major global engineering plastics manufacturers, such as BASF (brand Ultraform) and Polyplastics (brand DURACON), offer products with remarkably similar performance profiles.
For example, Polyplastics DURACON M270-44 grade also has an MFR of 27 g/10 min, and its technical data sheet lists mechanical and thermal properties that are nearly identical to those of Amcel KP30. Similarly, BASF’s Ultraform product line includes grades like W2320 003, which also feature very high flowability.
This finding has significant commercial and engineering implications. For procurement specialists, it means Amcel KP30 should be treated as a commodity subject to competitive bidding, where selection criteria, beyond technical performance, should focus on price, supply stability, technical support, and logistics services. For engineers, it means that in terms of supply chain risk management, there are direct, performance-interchangeable “second sources” available. If the supply of Amcel KP30 is disrupted, a switch to a competitor’s equivalent product can be made quickly, minimizing production risk.
High-Flow POM Copolymer Competitive Product Benchmark
Performance Parameter | Celanese Amcel KP30 | Polyplastics DURACON M270-44 |
MFR (g/10 min) | 27 | 27 |
Density (g/cm³) | 1.41 | 1.41 |
Tensile Modulus (MPa) | 2700−2800 | 2800 |
Tensile Stress at Yield (MPa) | 65 | 63 |
Charpy Notched Impact Strength (kJ/m²) | 5.0 | 5.3 |
HDT @ 1.8 MPa (°C) | 95−100 | 100 |
Acetal Copolymer Market Overview
The acetal copolymer market is a multi-billion dollar global industry, projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 5%−11% (data varies across market reports).
- Key Drivers: Market growth is primarily driven by two engines: the automotive industry’s continuous push for “lightweighting” to improve fuel efficiency and meet emissions regulations, and the steady demand from the electronics and consumer goods sectors for high-performance, precision-molded plastics.
- Price & Volatility: The production cost of POM is directly linked to the price of its upstream raw materials, such as methanol and formaldehyde. The prices of these base chemicals are significantly influenced by global energy markets, geopolitical factors, and macroeconomic conditions, leading to considerable volatility. This volatility is directly passed on to the final selling price of POM resin, posing challenges for cost control in long-term projects that rely on this material.
Conclusion & Strategic Recommendations
This report has conducted a detailed analysis of Amcel KP30, integrating its technical performance, processing characteristics, and market positioning to provide the following conclusions and strategic recommendations for professionals in related fields.
Value Proposition Summary
The core value of Amcel KP30 lies in its exceptional processing performance. When the primary design challenge is to achieve complex geometries, meet stringent thin-wall requirements, or when production efficiency (i.e., molding cycle time) is the key determinant of cost competitiveness, KP30 is the ideal material choice. It is suitable for applications that are satisfied with its good, but not top-tier, mechanical toughness. In short, it is a material born for “Design for Manufacturability.”
Design & Engineering Recommendations
To help engineers make more precise material selection decisions, the following checklist is recommended for evaluation. When your application meets most or all of the following criteria, Amcel KP30 should be given priority consideration:
Geometric Complexity: The part contains fine details, thin-walled structures (wall thickness can be less than 1 mm), or flow paths requiring long flow distances.
Cost Sensitivity: The project is highly sensitive to unit cost, and the efficiency gains from shorter injection molding cycles can translate into significant cost advantages.
Operating Temperature: The part’s continuous operating temperature under load is below 95℃.
Impact Environment: The application scenario does not involve high-energy, sharp impacts, or the part’s structural design can effectively mitigate impact stress concentrations.
Chemical Environment: The application requires the superior chemical resistance, hot water resistance, and alkali resistance characteristic of copolymers, which is superior to that of homopolymers.
Procurement & Manufacturing Recommendations
Procurement Strategy: Amcel KP30 should be treated as a standard industrial product with direct competitors. In procurement decisions, in addition to evaluating Celanese’s pricing and supply capabilities, quotes for its equivalent products (such as Polyplastics DURACON M270-44) should be actively sought for a comprehensive comparison of cost and supply chain risk. Establishing at least two qualified suppliers is an effective strategy for risk mitigation.
Operational Risk Management: Chemical incompatibility with PVC is the greatest “hidden” risk in production. If both materials are used within the same facility, the strictest material segregation, equipment cleaning, and changeover protocols must be established and enforced. The cost of a single contamination event, in terms of equipment downtime and repair, can be extremely high and must be given high priority at the operational level.
Safety First: All standard safety procedures for handling hot molten polymers must be mandatory. Ensure adequate ventilation in the injection molding machine’s barrel area to handle potential formaldehyde gas generated during process anomalies (e.g., overheating, excessive residence time). Before any processing operation, all relevant personnel must read and comply with the latest version of the official Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS).
