Polylactic acid (PLA) pellets are advancing sustainable manufacturing with their bio-based and biodegradable properties. Derived from renewable sources like corn starch, pla plastic pellets offer an industrially compostable alternative to traditional plastics, ideal for 3D printing, packaging, and more. The global PLA market, valued at approximately $1.4 billion in 2025, is projected to reach $5 billion by 2030 with a 15% CAGR, driven by demand for eco-friendly materials.
we supply high-quality pla plastic pellets tailored for 3D printing and packaging industries. Our polylactide resin supports vibrant PLA filament production and compostable packaging, aligning with global sustainability goals. This guide details the benefits, applications, and technical advantages of pla plastic pellets, empowering manufacturers to adopt sustainable solutions.
What Are PLA Pellets?
PLA pellets are small, uniform granules—typically 2 to 5 mm in diameter—made from polylactic acid (PLA) resin, a bio-based thermoplastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. As a plant-based alternative to fossil-fuel plastics, pla plastic pellets help reduce carbon emissions and support the global shift toward sustainable materials.
Chemically, PLA is an aliphatic polyester formed through ring-opening polymerization of lactide, which is obtained by fermenting plant sugars into lactic acid. The resulting resin is processed via melt extrusion, where molten PLA is cooled and cut into pellet form, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Due to its relatively low processing temperature, industrial compostability, and ease of molding or extrusion, PLA is selected for use in multiple application areas, including:
- 3D printing filaments, where PLA is valued for low warping and dimensional stability
- Sustainable packaging, such as food containers, films, and trays
- Compostable disposables, including cutlery and tableware
- Medical and agricultural products, where biodegradability is essential
By enabling the production of compostable goods, pla plastic pellets play a vital role in advancing circular economy goals, helping reduce landfill waste and environmental impact. Their growing adoption reflects rising demand for eco-conscious solutions in both local and international markets.

Key Benefits of Polylactic Acid Pellets
Polylactic acid (PLA) pellets offer significant advantages as a bioplastic, supporting sustainable manufacturing and aligning with global environmental standards. Their unique properties make them an ideal choice for businesses aiming to reduce their environmental impact while meeting market demand for eco-friendly products.
- Biodegradable and Compostable: PLA breaks down naturally in industrial composting facilities, reducing landfill waste and environmental impact.
- Renewable Sourcing: Derived from corn starch or sugarcane, PLA reduces reliance on fossil fuels, promoting a sustainable supply chain.
- Energy Efficiency: A lower melting point cuts energy use in production, lowering costs and emissions.
- Recyclable: PLA supports mechanical or chemical recycling, aligning with circular economy principles.
- Market Advantage: Using PLA meets consumer demand for eco-friendly products, enhancing brand reputation and regulatory compliance.
Adopting polylactic acid pellets enables manufacturers, to innovate in green technology, reduce carbon footprints, and address the global plastic waste crisis while staying competitive.

PLA vs Traditional Plastic Pellets
PLA (polylactic acid) pellets provide environmental and performance benefits over traditional plastics like polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), and ABS, ideal for sustainable applications like 3D printing and packaging.This section compares their properties to guide material selection.
| Property | PLA Pellets | PP Pellets | PE Pellets (HDPE) | ABS Pellets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable (corn, sugarcane) | Petroleum | Petroleum | Petroleum |
| Biodegradability | <6 months (industrial composting) | 100–1,000 years | 100–1,000 years | 100–1,000 years |
| Heat Deflection Temp (°C) | ~60 | 100–150 | 50–100 | ~100 |
| Impact Strength (kJ/m²) | ~5 | 20–40 | 10–20 | ~18 |
| Cost ($/kg) | 2–5 | <2 | <2 | <2 |

Environmental Advantages
polylactic acid pellets, made from renewable sources, biodegrade in <6 months under industrial composting, unlike PP, PE, and ABS, which persist for centuries (Filamentive). They emit 13.53%–62.19% less CO2 than traditional plastics (ScienceDirect).
Performance Advantages
PLA’s tensile strength (50–70 MPa) is comparable to PP and ABS (30–40 MPa), excelling in 3D printing and packaging. Its heat deflection temperature (~60°C) is lower than PP (100–150°C), PE (50–100°C), and ABS (~100°C), and impact strength (~5 kJ/m²) is below PP, PE, and ABS (Wevolver).
Limitations
PLA requires industrial composting to biodegrade; in landfills, it persists like traditional plastics (Reddit). Its heat sensitivity and higher cost ($2–5/kg vs. <2/kg) limit some applications (ResearchGate).
Applications of Polylactic acid
Polylactic acid pellets are versatile, supporting a range of eco-friendly applications due to their biodegradability and ease of processing. As a leading distributor, we supply high-quality polylactic acid pellets for industries seeking sustainable solutions.
3D Printing
polylactic acid pellets are widely used to produce PLA filament for 3D printing. Their low melting point (~60°C) and smooth extrusion enable precise, detailed designs for prototypes, models, and consumer products. Benefits include eco-friendly production, vibrant colors, and minimal warping, making pla plastic pellets a top choice for additive manufacturing .

Packaging
In packaging, pla resin create biodegradable films, containers, and bags that decompose under industrial composting conditions, reducing plastic waste compared to traditional plastics like PP and PE .
Healthcare
PLA is used in medical applications like biodegradable sutures and temporary implants. Its biocompatibility ensures safe use in the body, with environmentally friendly disposal. However, its low heat resistance limits use in high-temperature sterilization processes.
Other Applications
- Automotive: Limited use in low-stress, lightweight components due to PLA’s heat sensitivity (~60°C), which restricts broader adoption.
- Education: Pla pellets are used for affordable, safe educational models and tools, ideal for classroom prototyping .
- Agriculture: Biodegradable films for mulching support sustainable farming practices.
| Industry | Application | Benefits of Using PLA Pellets |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Printing | PLA filament for printers | Precise, eco-friendly, minimal warping |
| Packaging | Films, containers, bags | Biodegradable, reduces plastic waste |
| Healthcare | Sutures, temporary implants | Biocompatible, environmentally friendly disposal |
| Automotive | Lightweight components | Limited use, lightweight but heat-sensitive |
| Education | Models, prototyping tools | Affordable, safe for classroom use |
pla plastic pellets enable sustainable innovation across 3D printing, packaging, healthcare, and more. Their environmental benefits and versatility make pla resin a preferred choice for industries prioritizing eco-friendly solutions, supported by our reliable supply chain.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
polylactic acid offer significant environmental advantages over traditional plastics, supporting global sustainability through bio-based sourcing, compostability, and reduced emissions.Our PLA pellets meet EN 13432 compostability standards, ensuring quality and environmental responsibility.
| Aspect | PLA Pellets | Traditional Plastics (PP/PET) |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Renewable (corn, sugarcane) | Petroleum-based |
| Compostability | Yes (industrial, 55–70°C, <6 months) | No (100–1,000 years) |
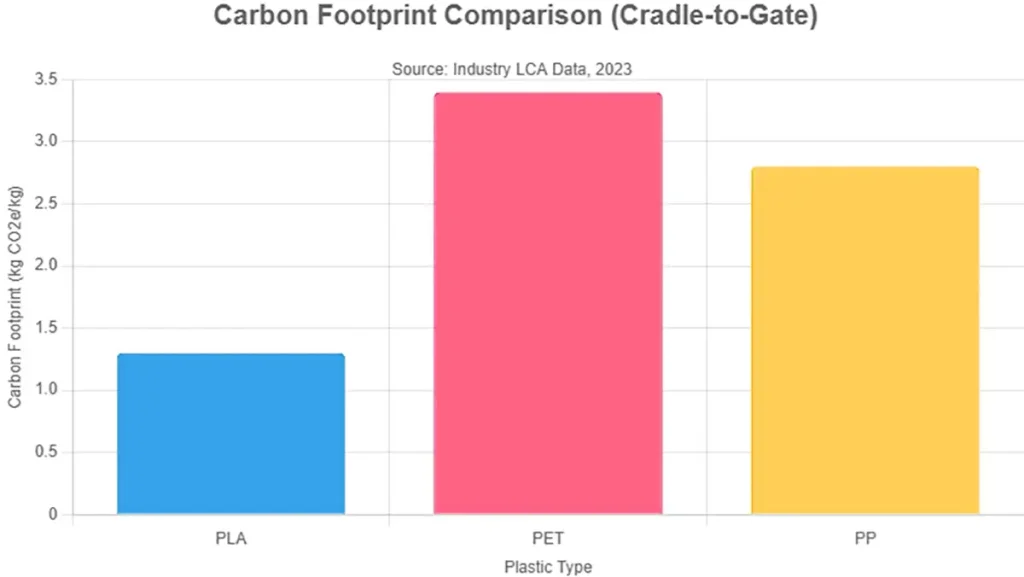
| Carbon Footprint | 1.24 kg CO2eq/kg (~60% lower than PET, ~22–38% lower than PP) | PP:2.8 kg CO2eq/kg, PET: 3.4 kg CO2eq/kg |
| Recycling | Mechanical/chemical (with separation) | Mechanical (widely available) |
Bio-Based Sources
Derived from corn starch or sugarcane, polylactic acid minimize reliance on fossil fuels, unlike petroleum-based PP and PET, supporting a sustainable bioeconomy.
Compostability
PLA pellets biodegrade in under 6 months under industrial composting conditions (55–70°C, specific bacteria). They do not degrade in home composting or landfills, requiring proper facilities (Filamentive).
Carbon Footprint
PLA production emits 1.24 kg CO2eq/kg, ~60% less than PET (3.4 kg CO2eq/kg) and ~22–38% less than PP (1.8–3.0 kg kg CO2eq/kg), per NatureWorks’ LCA and industry studies (NatureWorks; ScienceDirect).
Recycling Potential
PLA support mechanical and chemical recycling but require separation from other plastics to avoid contamination (PMC).
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of PLA enable manufacturers to select materials that ensure precision in extrusion, molding, and other processes while meeting environmental standards. Derived from renewable resources, polylactic acid pellets offer consistent density, strength, and flow properties, supporting efficient production of lightweight, biodegradable products. These specifications, verified by industry certifications, guide professionals in choosing pla plastic pellets for reliable, eco-friendly manufacturing outcomes.
Specifications Table
| Property | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.2–1.25 g/cm³ | Reduces material use in lightweight designs. |
| Melting Point | 150–180°C | Compatible with standard extrusion equipment. |
| Glass Transition Temperature | 55–60°C | Restricts use above 60°C due to softening. |
| Tensile Strength | 50–70 MPa | Supports structural integrity in low-stress products. |
| Melt Flow Index | 5–20 g/10min | Tailored for extrusion or molding processes. |
Specialized Grades and Customization
PLA pellets are available in high-transparency grades for clear films, toughened grades for improved durability, and food-safe grades for utensils, certified under FDA standards. Customization with colorants, plasticizers, or heat-resistant blends allows precise tailoring to manufacturing requirements.
Compliance and Storage
Certified under EN 13432 and ISO 14855, pla biodegrade in under 6 months in industrial composting facilities (60°C, specific bacteria). Store in a cool, dry environment to prevent moisture degradation. As a leading distributor, we supply high-quality pla resin in pellet form to meet global manufacturing standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q:PLA resin, a bio-based, compostable bioplastic, has a 60% lower carbon footprint than ABS but lower heat resistance (melts at 150–180°C vs. ABS’s ~200°C) and impact strength (50–70 MPa vs. 40–60 MPa). PLA suits eco-friendly packaging and 3D printing; ABS is better for durable, heat-resistant parts like automotive components.
Q:Yes, our PLA polymer pellets include food-grade options certified to FDA and EU 10/2011 standards, safe for food packaging like containers. Contact us for certification details.
Q: Yes, we did. Check out this article: “PLA Recycling: A Comprehensive Guide”.
A:Did you talk about PLA recycling?
Q:PLA resin pellets work with FDM 3D printers with pellet extruders (e.g., BigRep STUDIO, 3devo Composer) or can be processed into filament for printers like Creality Ender-3. Use extruder temperatures of 180–210°C.
Q:Store PLA polymer pellets in a cool, dry place (<25°C, <50% humidity) in sealed containers to prevent moisture absorption. Process at 180–210°C for extrusion or 3D printing, ensuring good ventilation to avoid degradation.
Q:Yes, PLA resin is biodegradable under industrial composting conditions (55–70°C, 90% humidity, per ASTM D6400). It is not suitable for home composting but reduces environmental impact compared to petroleum-based plastics.
Q:PLA suits eco-friendly 3D printing and packaging; PETG excels in durable, flexible parts like medical containers.Please see PETG vs PLA: Key Differences, Pros and Cons, and Best Use Cases.
Conclusion
PLA resin is a bio-based, compostable bioplastic with a 60% lower carbon footprint than PET, ideal for 3D printing, food packaging, and medical applications. Its uniform pellets ensure consistent performance in manufacturing. The PLA polymer market is expected to reach $20 billion by 2030, driven by demand for sustainable packaging and durable blends for automotive and electronics. Certified for industrial composting (ASTM D6400), PLA supports greener production.
If you have questions about Polylactic Acid (PLA) or our products, get in touch. You can email us at jerry@salesplastics.com or call +8618657312116. We’re here to help.




