Achieving micron-level precision in components with ultra-thin walls and complex geometries is a perennial challenge in precision engineering. Material flow properties and chemical stability often dictate the feasibility and long-term reliability of such parts. POM M90, a specialized acetal copolymer, is specifically engineered to meet this demanding requirement. Its exceptional high-flow characteristics enable manufacturers to significantly reduce cycle times and achieve superior filling capabilities in challenging molds. Crucially, its enhanced alkali resistance (chemical resistance) extends product life and functional integrity in environments where standard acetal grades would degrade. For the engineer grappling with stringent dimensional stability and mechanical strength targets, or the procurement team seeking optimal processing efficiency and material value, understanding the convergence of these unique properties in POM M90 is vital for making an informed, technically sound decision.
What is POM M90?
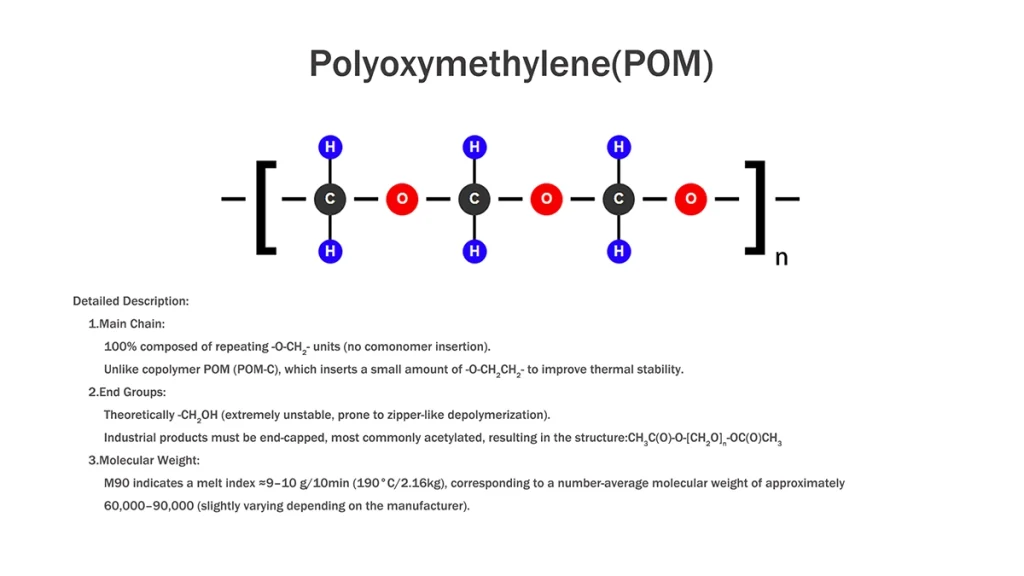
POM M90 is a medium-viscosity polyoxymethylene copolymer, precisely formulated for injection molding applications that require both high precision and excellent processing throughput. The “M90” designation typically corresponds to its targeted Melt Volume Rate (MVR), which is optimized to balance mold-filling efficiency (high flow) with maintained mechanical integrity (strength).
This specific grade utilizes a tailored molecular weight distribution, facilitating fast cycle times and superior filling of intricate or thin-walled mold cavities—a feature critical for achieving tight dimensional stability tolerances.
From a chemical perspective, POM M90 retains the standard acetal polymer backbone of oxymethylene (-CH₂O-) units. However, it incorporates specific comonomers, strategically integrated during polymerization, to interrupt the regularity of the chain. This structural modification is key; it significantly enhances thermal stability and, most importantly, provides superior resistance to chemical degradation from alkaline substances. This copolymer architecture directly mitigates the “unzipping” depolymerization mechanism common in homopolymer POM, translating to greater longevity and reliability in harsh operating environments.
Why Thin-Wall Precision Molding Demands POM M90
Thin-wall molding is a strategic necessity in product design, enabling the reliable manufacture of components with wall sections often below 0.8 mm while rigorously maintaining complex geometries and sub-millimeter tolerances. The success of this advanced process is highly dependent on the chosen material’s processability. POM M90’s high-flow characteristics are often a prerequisite for realizing the core advantages of thin-wall precision:
Material Efficiency
Thin-wall construction typically yields a 25% to 40% reduction in required material volume compared to conventional designs. Utilizing POM M90’s high melt flow minimizes pressure drop across the mold cavity, preventing costly incomplete fills (shorts) and maximizing yield from every pound of resin.
Integrated Part Miniaturization
In rapidly evolving sectors like consumer electronics and medical devices, thin-walling allows for increased part density and functional integration. POM M90’s flowability ensures that intricate features and small mounting points are fully formed, which is critical for components requiring complex assembly.
Enhanced Thermal Management and Cycle Efficiency
The reduced mass of thin-walled parts allows for significantly accelerated cooling rates. Crucially, POM M90’s superior flow allows for a faster injection rate, complementing the rapid cooling by minimizing hold time and resulting in a measurable reduction in total cycle time.
Mass Reduction for Performance
For industries driven by weight constraints (e.g., e-mobility, portable technology), thin-wall designs directly support aggressive lightweighting strategies. Components molded from M90 maintain excellent specific stiffness and strength, ensuring structural integrity is preserved despite the mass reduction.
The intrinsic value of POM M90 in this context lies in its dual capability: achieving full mold filling in extreme thin-wall sections while simultaneously offering the controlled, low shrinkage required to guarantee ± 0.05 mm dimensional stability after ejection.

Application scope: Applications of POM M90
The specific engineering profile of POM M90—combining its high-flow processing advantage with superior dimensional stability and enhanced chemical resistance—enables solutions in demanding, high-volume sectors. The following examples illustrate how M90 translates technical performance into functional component reliability:
Automotive
- Fuel System Components: Utilizing enhanced alkali resistance for precise fittings and pump housings exposed to aggressive fuels.
- Precision Drive Components: Optimized for low-friction gears and bearings in systems like window regulators.
- Integrated Fasteners: High-flow properties enable rapid molding of thin-wall, secure snap-fit clips.
Consumer Electronics
- Miniaturized Housings: Excellent flow for intricate internal brackets and thin-wall connector bodies in smartphones and laptops.
- Motion Mechanisms: Ensuring long-term, reliable operation for laptop hinge assemblies due to POM’s fatigue and wear resistance.
- Optical Components: High precision for camera lens motion parts requiring tight optical alignment.
Medical Devices
- Dosing Systems: Low extractability and high precision for components in insulin pens and metered-dose inhalers.
- Fluid Management: Rapid production of manifolds and valves requiring chemical compatibility and critical internal channel tolerances.
- Surgical Instruments: Providing precise dimensional stability for critical reusable and single-use parts.
Industrial Automation & Fluid Control
- Valve Bodies & Pistons: Stability under pressure and improved processing for complex solenoid and pneumatic valve components.

Need Application-Specific Guidance?
Our technical team can provide detailed recommendations for your specific application requirements. Contact us for personalized material selection assistance.
Technical Specifications
The material properties detailed below provide the quantitative basis for POM M90’s capability in high-precision, thin-wall applications. This technical profile should be viewed in conjunction with the specific requirements of the application, focusing particularly on the balance between flow rate, mechanical strength, and dimensional control.
| Property | Test Method | Unit | M90-57 WK2001 | M90-44 | Insight |
| Flow Rate (MVR) | ISO 1133 | cm³/10min | 8 | 8 | High flow confirmed for thin-wall molding |
| Density | ISO 1183 | g/cm³ | 1.41 | 1.41 | Consistent density profile |
| Shrinkage (Flow) | ISO 294 | % | 1.9 | 2 | Critical value for mold design |
| Shrinkage (xFlow) | ISO 294 | % | 2.9 | 2 | M90-44: Minimal Anisotropy (Low Warpage) |
| Water Absorption | ISO 62 | % | 0.5 | 0.5 | Low moisture uptake, high stability |
| Tensile Modulus | ISO 527 | MPa | 2700 | 2500 | M90-57 offers higher rigidity |
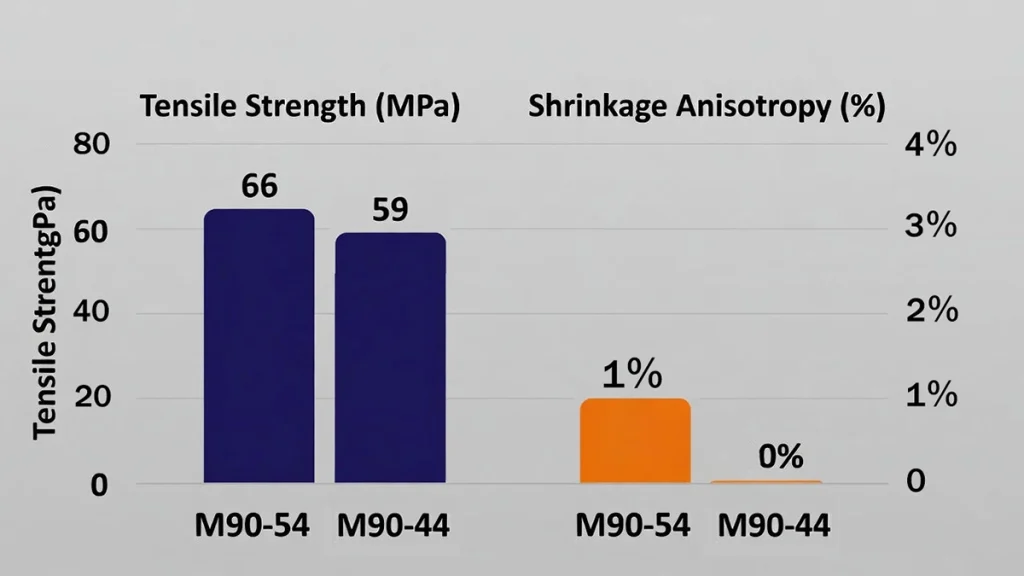
| Tensile Strength | ISO 527 | MPa | 66 | 59 | M90-57: Higher ultimate strength |
| Elongation at Break | ISO 527 | % | 35 | 40 | Indicates material toughness |
| Flexural Modulus | ISO 178 | MPa | 2500 | 2350 | Bending rigidity |
| Charpy Notch Impact | ISO 179 | kJ/㎡ | 9 | 8 | Impact resistance |
| Rockwell Hardness M | ISO 2039 | Scale | 86 | 80 | Surface hardness |
| HDT 1.8 MPa | ISO 75 | ℃ | (N/A) | 90 | Thermal stability under load |
Key Technical Takeaways:
- High-Flow Consistency: Both grades feature an MVR of 8 cm³/10min, confirming their suitability for high-speed, thin-wall injection molding.
- Dimensional Control (Shrinkage):
- M90-44: Exhibits near-zero shrinkage anisotropy (flow vs. transverse ≈ 2.0% vs 2.0%), making it the superior choice for components that must maintain ultra-flatness and minimal warpage.
- M90-57: Shows a higher shrinkage differential (1.9% vs 2.9%), requiring careful mold design compensation, but delivers higher mechanical strength (Tensile Strength 66 MPa vs 59 MPa).
- Wear Performance: The detailed wear data (Specific Wear Rate) provided for M90-57 and M90-44 should be pulled into a separate, dedicated section if your target audience focuses on gears or bearings, as this level of detail is highly specialized and valuable.
Need Complete Technical Data?
Download our comprehensive technical data sheet for detailed specifications, processing parameters, and performance characteristics of POM M90.
Core Advantages
POM M90 is specifically formulated to overcome the processing and durability limitations often encountered with commodity acetal grades. By leveraging its copolymer structure and high MVR profile, M90 provides tangible engineering benefits, making it the robust solution for high-precision demands:
Key Advantages of POM M90
- Superior Melt Flow Efficiency: Enables full and rapid mold filling of intricate, thin-wall geometries (down to 0.5 mm).
- Enhanced Alkalinity Resistance: The copolymer structure provides up to 30% improved resistance to strong alkaline solutions and high-pH environments.
- Dimensional Control & Low Warpage: Exhibits controlled, low shrinkage anisotropy, essential for maintaining sub-millimeter tolerances.
- Optimized Mechanical Integrity: Retains high stiffness (Tensile Modulus ≈ 2700 MPa) despite its enhanced flowability.
- Consistent Process Window: Features low plate-out and reduced volatile emissions, ensuring stable, predictable injection molding consistency.
- Low Friction and Wear: Inherent self-lubricating properties deliver high performance for demanding gears and moving mechanisms.
Comparison with Other Materials
Material specification requires a critical assessment of performance trade-offs against cost and processing efficiency. To determine when POM M90 is the optimal choice, the following comparison highlights its distinct position among standard acetal, high-strength polyamides, and general-purpose resins:
| Property | POM M90 (High-Flow Copolymer) | Standard POM-C | POM-H | PA66 | ABS |
| Melt Flow Characteristics | Excellent (High MVR) | Good | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 66 | 60 | 70 | 85 | 45 |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent (Low Warpage) | Good | Excellent | Moderate | Good |
| Alkali/Chemical Resistance | Very Good | Good | Moderate | Poor | Good |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Poor |
| Moisture Absorption | Very Low | Very Low | Very Low | High | Low |
| Thin-Wall Capability | Excellent | Good | Moderate | Good | Very Good |

- Precision and Throughput are Critical: M90 provides the necessary high flow for thin-wall molding without sacrificing dimensional control, outperforming POM-H and standard POM-C in complex geometries.
- Alkaline Exposure is Present: M90‘s copolymer structure delivers crucial resistance to strong bases, unlike POM-H (which is susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis) or PA66 (which suffers in both alkaline and acidic environments).
- Low Moisture Sensitivity is Required: Unlike PA66 (Nylon), M90 maintains consistent mechanical and dimensional properties regardless of humidity exposure, ensuring reliability in applications like medical devices and fluid handling.
Processing Guidelines
To fully leverage POM M90’s high melt flow and achieve consistent performance in thin-wall, high-precision applications, adherence to optimal processing and mold design principles is essential.
Recommended Processing Parameters
| Parameter | Range (Recommended) | Unit | Rationale |
| Melt Temperature | 190 – 210 | °C | Maintains low melt viscosity. Avoid exceeding 220°C to prevent material degradation. |
| Mold Temperature | 80 – 100 | °C | Higher temperatures (around 90°C) promote laminar flow, improve surface replication, and enhance dimensional stability. |
| Injection Pressure | 80 – 120 | MPa | High pressure is often necessary to compact thin sections and achieve tight tolerance. |
| Injection Speed | Medium to High | – | High speed is recommended for thin-wall molding to maintain melt temperature and prevent premature solidification (freeze-off). |
Mold Design Considerations for Thin-Wall Applications
Mold design must compensate for the material’s high flow and propensity for flashing.
Wall Thickness & Transitions
- Minimum recommended thickness: 0.5 mm.
- Thickness transitions should be gradual, maintaining a ratio of 3:1 or less to minimize stress concentration.
- Rib thickness should ideally be 60% to 80% of the nominal wall thickness.
Gate System
- Fan or Film Gates are recommended for thin-wall sections to ensure even fill distribution.
- Gate thickness should be 40% to 60% of the nominal wall thickness.
- Avoid pin gates in thin sections to prevent jetting and flow marks.
Venting
- Venting is critical due to the rapid fill speed. Vent depth should be precise 0.01 mm to 0.02 mm).
- Place vents at the end-of-fill areas and at all potential air traps.
- Vacuum venting should be considered for highly complex or ultra-thin geometries.
Runner System
- Full-round runners (Ø 4 mm to 6 mm) are preferred. A balanced runner system is mandatory for multi-cavity molds to ensure uniform pressure and material distribution.
Processing Tip: WWhen molding thin-wall parts, the best results are achieved using a sequential (or stepped) injection profile. Initiate filling with a high speed to quickly fill the thin cavity (leveraging M90’s high MVR), followed by a controlled decrease in velocity. This technique minimizes shear heating near the gate while maintaining sufficient pressure at the flow front, optimizing both surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Supply Information
Ensuring uninterrupted supply and flexible fulfillment is critical for continuous high-volume production. We serve as a specialized source for the High-Flow M90 grade, offering material from leading global manufacturers, including Polyplastics, Celanese, and others, to match your specific performance and sourcing requirements.
As authorized distributors, we offer various packaging and format options structured to seamlessly integrate with diverse manufacturing and testing requirements:
| Form | Packaging Options | Standard Color Availability | Customization & Lead Time |
| Virgin Pellets | Standard bags | Natural (Standard White) and Black | Typically held in stock at regional distribution centers for immediate fulfillment. |
| Custom Pre-colored Grades | Standard bags (MOQ applies) | Custom RAL or Pantone matching | Available upon request. Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) and specific lead times apply due to specialized compounding runs. |
| Testing & Sampling | Standard injection-molded test plaques or smaller pellet quantities | Natural (Standard White) | Available through our technical service team for qualification purposes. |
Fulfillment and Support:
For project initiation, our technical team can provide samples for initial testing. For high-volume production, our supply chain is structured to offer JIT (Just-In-Time) delivery and tailored logistics solutions. Please contact our sales office to discuss pricing and lead times based on your specific annual consumption and chosen brand’s grade Polyplastics M90, Celanese M90, etc.).
Ready to Order POM M90 for Your Application?
Contact our technical sales team for pricing, availability, and technical support. We offer competitive pricing and global logistics solutions for both small-scale testing and full production requirements.

Conclusion
POM M90 defines the standard for next-generation polyacetal solutions, addressing the critical manufacturing demands of today. Its unique high-flow MVR (≈ 8 cm³/10min) ensures the successful molding of complex, thin-wall components where POM-H or commodity grades would fail to fill.
For technical professionals, POM M90 offers a strategic advantage: the material successfully integrates high mechanical stiffness with essential copolymer benefits, notably enhanced resistance to alkaline degradation and the ability (especially M90-44) to achieve near-perfect dimensional stability and flatness. M90 is the proven choice when the application requires uncompromised throughput, precision, and long-term chemical reliability.
Ready to Optimize Your Next Project with POM M90?
Our technical team is available to provide detailed specifications, processing guidance, and application-specific recommendations. Contact us today to discuss how POM M90 can enhance your engineering solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between POM and POM-H?
POM is split into Homopolymer (POM-H) and Copolymer (POM-C, like M90). POM-H offers slightly higher peak tensile strength. POM-C (M90) provides superior resistance to alkaline substances and better thermal stability, which translates to a more stable processing window.
Is POM the same as Delrin?
No. Delrin® is Celanese’s registered trade name for their POM Homopolymer POM-H products. While both are polyacetals, Delrin is known for maximum stiffness and strength, whereas POM M90 (a copolymer grade) is optimized for superior alkaline resistance, better flowability, and improved processing stability.
What are the properties of POM M90 44 material?
M90-44 is an M90 variant focused on maximal dimensional consistency. Its key feature is its minimal shrinkage anisotropy (2.0% Flow vs. 2.0% Transverse), making it the ideal choice for large, thin components requiring the tightest possible warpage control and flatness.
What is the difference between nylon and POM?
The critical difference is moisture absorption. POM has very low moisture uptake (≈ 0.2%), ensuring reliable dimensional stability. Nylon (PA66) absorbs significantly more moisture (≈ 1.5 – 3.0%), causing dimensional and electrical properties to shift in humid environments. POM also generally offers better wear and stiffness.
Is POM stronger than ABS?
Yes, POM is generally stronger and far more rigid than ABS. POM offers higher Tensile Strength (≈ 66 MPa) and superior wear resistance, hardness, and fatigue life. ABS typically only surpasses POM in impact resistance at room temperature and lower cost.
What does POM stand for in plastic?
POM stands for PolyOxyMethylene. It is widely recognized as Polyacetal or simply Acetal. Key commercial brands supplying this material include DURACON (Polyplastics), Celcon (Celanese), and Hostaform (Celanese).



