Polyplastics Duranex 2002 defines the technical baseline for Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) resin. This standard unfilled grade serves a specific engineering purpose distinct from reinforced counterparts: it prioritizes dimensional precision and surface integrity over raw mechanical load.
Glass-fiber grades often compromise surface finish and warp resistance to achieve stiffness. Duranex 2002, conversely, delivers a calibrated balance of moldability, aesthetic quality, and electrical consistency. This guide analyzes whether the material’s focus on isotropic stability aligns with your specific design criteria.
Material Profile: Defining Duranex 2002
Before evaluating performance, engineers require a precise understanding of the material’s composition and compliance profile. Duranex 2002 is a standard-grade PBT defined by its inherent polymer structure and established regulatory status.
Duranex 2002 is based on Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT), a crystalline, linear thermoplastic polyester. This polymer structure is synthesized from terephthalic acid and 1,4-butanediol. PBT’s high melting point, high degree of crystallinity, and inherently low water absorption coefficient are the foundation for its superior dimensional stability and excellent electrical properties—even before any reinforcement is considered.
Core Product Specifications
This grade is specified as the foundational standard of the Duranex lineup, designed for general-purpose applications where moldability and consistency are paramount.
| Specification | Description | Technical Note |
| Filler Status | Unfilled (Pure Resin) | Density = 1.31 g/cm³ |
| Viscosity | Standard/Medium Viscosity | Balances flow for moldability with mechanical properties. |
| Toughness | General Purpose, High Toughness | Offers high elongation at break (≈ 50% nominal strain) compared to brittle reinforced grades. |
Regulatory & Flammability Compliance
Compliance is non-negotiable for target industries, such as Electrical/Electronic and Automotive. Duranex 2002 maintains industry-standard compliance that supports its use in mass-market applications:
UL 94 Flammability
Rated HB (Horizontal Burning). This is the expected classification for an unreinforced, standard PBT grade, indicating a slow burning rate on a horizontal specimen. (UL File No. E213445).
Environmental Compliance
Complies with modern standards like RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), supporting its use in global consumer and electronic supply chains.
Performance Architecture: Why Choose Duranex 2002?
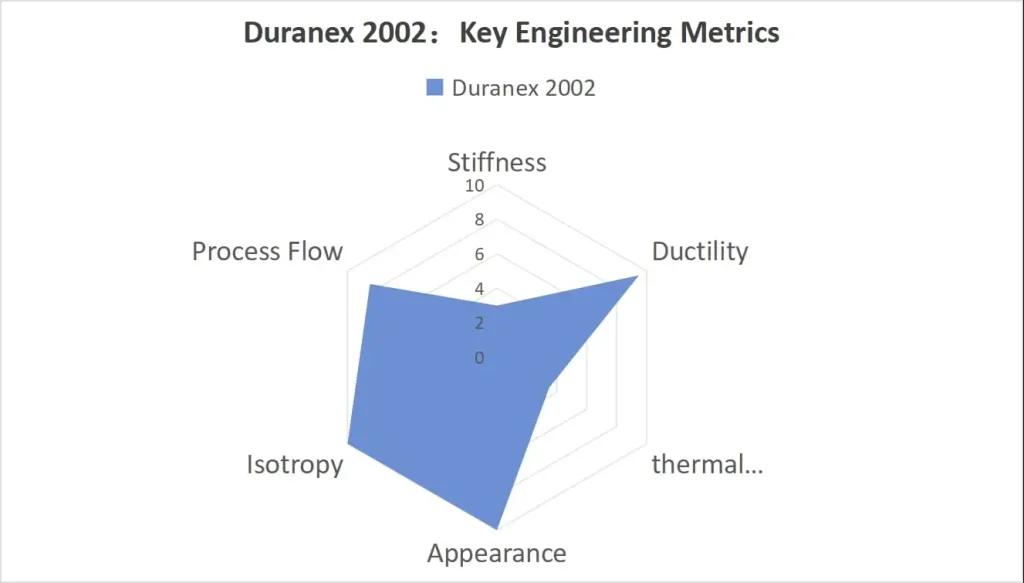
Duranex 2002 is fundamentally specified by engineers seeking a structurally sound polymer that prioritizes consistency and processability. Its performance profile is not about achieving extreme metrics in a single dimension, but about delivering a robust and predictable combination of mechanical, thermal, and electrical integrity.
Mechanical Integrity
This unreinforced grade offers a strategic balance between toughness and rigidity, mitigating the inherent brittleness common in highly-filled systems.
- Stiffness: The material provides a strong baseline with a Flexural Modulus of approximately 2630 MPa.
- Structural Strength: Tensile Strength reaches up to 60 MPa, ensuring structural reliability under typical load-bearing conditions.
- Impact Resistance: Significantly, it offers high elongation (up to 50% nominal strain), which is critical for resisting brittle failure and absorbing energy in components subjected to dynamic stress or assembly snap-fits.
Thermal and Dimensional Consistency
Duranex 2002 delivers the thermal stability necessary for components exposed to elevated temperatures and thermal cycling.
- Thermal Resistance: It maintains dimensional stability up to a Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) of 70°C (at 1.8MPa load).
- Predictable Expansion: The consistent Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE), typically 110×10⁻⁶/K, allows for precise tolerance stacking and reliable design calculations in assemblies where metal or other polymers are used.
Electrical Insulation and Safety
The material’s pure polymer structure ensures exceptional electrical isolation, positioning it for critical E&E applications where safety is non-negotiable.
- Insulation Capability: Demonstrated by a high Volume Resistivity (typically 5×10¹⁴Ω·cm) and Dielectric Strength (14 kV/mm).
- Arc and Tracking Resistance: Its impressive Comparative Tracking Index (≥ 600 V) is crucial for preventing electrical breakdown and ensuring long-term safety in components exposed to surface contaminants and high voltages.
Surface Aesthetics and Processability
The combination of optimized flow and inherent purity makes 2002 the grade of choice for visible parts.
- Aesthetic Finish: High-gloss surface finish is achieved directly from the mold, eliminating secondary finishing operations.
- Dimensional Quality: Its excellent flow characteristics and rapid crystallization rate contribute to short cycle times, precise dimensions, and minimal, isotropic warpage, a crucial factor for aesthetic housings and coupling components.
Chemical Resistance
Duranex 2002 provides reliable long-term performance through its inherent chemical stability. It exhibits excellent resistance to common environmental agents, including hydrocarbons, automotive oils, greases, and many weak acids, safeguarding component integrity in demanding service environments.
Technical Specifications Snapshot
This section provides a concise summary of the key technical metrics for the Duranex 2002 standard unfilled grade, establishing the material’s data-driven foundation for dimensional stability and processing consistency.
| Physical Properties | Value | Unit | Test Method |
| Density | 1310 | kg/m³ | ISO 1183 |
| Tensile Strength | 60 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Elongation Break | 50 | % | ISO 527 |
| Flexural Modulus | 2630 | MPa | ISO 178 |
| Thermal Properties | Value | Unit | Test Method |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (1.8 MPa) | 70 | °C | ISO 75 |
| CLE Flow 23~55°C | 1.1E-4 | cm/cm/°C | INTERNAL METHOD |
| CLE xFlow 23~55°C | 1.1E-4 | cm/cm/°C | INTERNAL METHOD |
| Electrical Properties | Value | Unit | Test Method |
| Volume Resistivity | 5E+16 | Ω.cm | IEC 60093 |
This data set represents the pure, unadulterated performance of the PBT polymer. Engineers should note two critical factors that define the unreinforced baseline:
- High Ductility: The 50% Elongation at Break is significantly higher than that of glass-filled PBT grades. This indicates superior toughness and the material’s ability to withstand deformation, making it ideal for parts requiring snap-fit functionality or resistance to impact-induced cracks.
- Isotropic Consistency: The Coefficient of Linear Expansion (1.1×10⁻⁴/℃) is consistent across all directions. This consistency is the data-driven evidence of the material’s uniform shrinkage, guaranteeing the predictability required for precision molding and low warpage in high-tolerance components.
Access Complete Technical Specifications
Download the comprehensive technical data sheet for Duranex 2002 with detailed property values, processing parameters, and compliance information.
Comparative Selection Strategy: Duranex 2002 vs. 3300 (GF30)
Selecting the optimal PBT grade requires a clear understanding of the design trade-offs between the unfilled baseline and its reinforced counterparts. The comparison below, using the 30% glass-fiber reinforced Duranex 3300 (GF30) as a reference, highlights the performance distinctions that guide the material specification process.
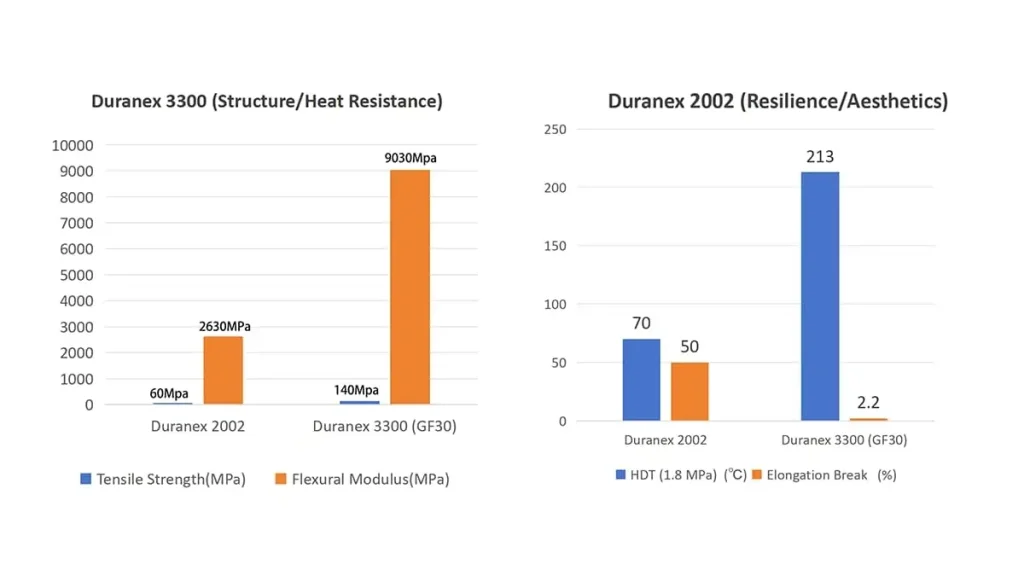
| Property | Duranex 2002 (Unfilled) | Duranex 3300 (GF30) | Design Implications |
| Tensile Strength | 60 MPa | 140 MPa | GF30 provides >2x structural load capacity. |
| Flexural Modulus | 2630 MPa | 9030 MPa | GF30 provides >3x higher stiffness for load-bearing. |
| HDT (1.8 MPa) | 70°C | 213°C | GF30 offers significantly higher thermal resistance and creep stability. |
| Elongation Break | 50% | 2.2% | 2002 delivers high ductility and impact tolerance. |
| Surface Finish | Pristine, High-Gloss | Fair (Fiber visible) | 2002 is required for aesthetic surfaces. |
| Dimensional Stability | Isotropic (Low Warpage) | Anisotropic (Moderate Warpage) | 2002 minimizes distortion in flat or complex geometries. |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | 2002 provides a material cost advantage. |
Application-Specific Selection Guidance
Choose Duranex 2002 When:
- Aesthetics and Finish Quality are the primary external requirements.
- Ductility, impact absorption, or resilient snap-fit features are necessary.
- Complex Geometries or thin-walled parts require maximum flow and uniform shrinkage.
- Tightly Toleranced components require isotropic dimensional stability (minimal warpage).
- Cost Optimization is prioritized over maximum structural performance.
- Operating temperatures remain strictly below 70℃ under load.
Choose Duranex 3300 (GF30) When:
- High Mechanical Load and sustained structural rigidity are required.
- Elevated Temperature Performance (up to 210°C HDT) is essential.
- Creep Resistance and long-term stability under stress are critical.
- Modulus-to-Weight Ratio is a key metric for lightweight structural parts.
- The design can accommodate anisotropic shrinkage and potential fiber flow lines on the surface.
- Applications involve significant thermal cycling where high HDT provides an advantage.
Need Expert Material Selection Guidance?
Our technical specialists can help you determine whether Duranex 2002 or another grade is optimal for your specific application requirements.
Primary Applications of Duranex 2002
Duranex 2002’s calibrated property profile makes it the material of choice when precision, electrical isolation, and surface quality must align with reliable mechanical performance. Its stability serves as a foundational element across the following core industries:

Diverse industrial components manufactured using Duranex 2002 PBT resin
Electrical & Electronics

- Connector housings and terminal blocks
- Relay and switch components
- Coil formers and bobbins requiring thin walls
- High-CTI insulating components
Automotive

- Sensor housings and protective covers
- Electrical distribution boxes (fuse boxes)
- Wiper system components and small gear trains
- Interior cosmetic parts (e.g., mirror housings)
Consumer & Industrial

- Precision pump and valve components
- High-gloss appliance enclosures and visible consumer touchpoints
- Mechanical parts requiring ductility and complex molding
- Housing components where low warpage is non-negotiable
Processing & Engineering Guide
Achieving the inherent performance and precision of Duranex 2002 requires stringent control over material preparation and injection molding parameters. Adherence to these guidelines is critical for maximizing part quality, minimizing warpage, and ensuring efficient production.
Pre-Processing: Drying Protocols
Proper drying is non-negotiable for PBT to prevent hydrolytic degradation (reduction of molecular weight) during the high-temperature molding process. The following protocols ensure optimal resin integrity:
| Parameter | Recommended Value | Technical Objective |
| Drying Temperature | 120℃ to 130℃ | Activate moisture removal efficiently. |
| Drying Time | 4 to 6 hours | Necessary duration to reach target moisture level. |
| Moisture Content Target | <0.04% | Absolute maximum moisture content before processing. |
| Drying Method | Dehumidifying dryer | Mandatory for consistent, low dew-point air. |
| Storage | Keep in sealed containers | Protect dried resin from ambient humidity. |
Molding Parameter Reference
The following are the typical reference values required to achieve optimal melt homogeneity, flow, and crystallization rates for Duranex 2002:
| Processing Parameter | Recommended Value | Unit | Notes |
| Mold Temperature | 75 | °C | Range: 60-80°C to ensure fast, complete crystallization and dimensional stability. |
| Melt Temperature (Nozzle) | 245-250 | °C | Optimal flow; maintain progressive profile (Zone 1: 200°C, Zone 3: 240°C). |
| Injection Speed | Moderate (40-60) | mm/s | Balanced filling; avoid excessively high speeds to prevent shear heating/degradation. |
| Holding Pressure | 60-80% of Injection | % | Essential for density packing, minimizing sink marks and voids. |
| Screw Speed | Low to Moderate | rpm | Minimize friction-induced shear heat and potential polymer chain scission. |
Design Considerations
For applications leveraging the precision of Duranex 2002, the following engineering guidelines are paramount:
Uniform Wall Thickness
Maintain a consistent wall thickness, ideally between 1.0-3.0mm. Wall variations exceeding 25% must incorporate gradual transitions to manage differential shrinkage and prevent warpage.
Draft Angles
Implement minimum Draft Angles of 0.5° per side for textured surfaces and 0.3° for smooth surfaces. This is critical for reliable part ejection and preserving the high-gloss finish.
Rib Design
To support structural integrity and minimize cosmetic sink marks, use ribs with a thickness of 0.5-0.6 times the nominal wall thickness.
Gate Design & Placement
Pin gates (0.8-1.2mm diameter) or Fan gates are preferred. Gate onto the thickest section of the component to ensure uniform filling and minimize flow-line visibility.
Conclusion & Supply Assurance
Duranex 2002 delivers a critical, non-negotiable role in the PBT market: it is the unfilled technical baseline against which all other grades are measured. This guide has demonstrated that its core value lies not in maximum strength, but in providing isotropic stability, predictable electrical performance, and an uncompromised surface finish.
The material’s defining features—high ductility, low warpage, and consistent processing—make it the optimal, cost-effective solution for precision-driven applications. Where structural demands exceed the 70°C HDT or 60 MPa strength baseline, high-performance alternatives like the glass-fiber reinforced Duranex 3300 stand ready to meet enhanced requirements.
Technical Support and Supply Commitment
As your dedicated PBT resin partner, we understand that material sourcing is inseparable from technical success. We ensure reliable supply of Duranex 2002, supported by deep application expertise and direct access to Polyplastics’ full technical data.
Experience Duranex 2002 Performance
Request material samples for testing and evaluation in your specific application. Our technical team is available to provide processing guidance and application support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is PBT used for?
- Electrical components (connectors, terminal blocks, switch housings)
- Automotive parts (sensor housings, electrical components, small gears)
- Consumer electronics (structural components, housings)
- Industrial equipment (pump components, precision parts)
- Appliance components (structural and functional parts)
Is PBT the same as PET?
- Crystallization Rate: PBT crystallizes much faster than PET, enabling shorter molding cycles
- Melting Point: PBT has a lower melting point (225°C) compared to PET (255°C)
- Water Absorption: PBT absorbs less moisture than PET
- Processing: PBT is easier to process in injection molding applications
- Applications: PET is commonly used in packaging and fibers, while PBT excels in engineering applications
What are the grades of PBT?
- Unfilled Grades: Like Duranex 2002, offering balanced properties for general applications
- Glass Fiber Reinforced: Grades with 15-50% glass fiber (e.g., Duranex 3300) for increased strength and stiffness
- Flame Retardant: Grades with additives to meet UL94 V-0 or V-2 ratings
- Impact Modified: Grades with elastomeric additives for improved impact resistance
- Mineral Filled: Grades with mineral fillers for dimensional stability and reduced warpage
- Heat Stabilized: Grades with additives for improved performance at elevated temperatures
- Hydrolysis Resistant: Grades with enhanced resistance to moisture degradation
Is PBT the same as polyester?
- PBT is a specific type of thermoplastic polyester made from butanediol and terephthalic acid
- Other common polyesters include PET (polyethylene terephthalate), PCT (polycyclohexylene terephthalate), and various copolyesters
- Polyester can also refer to thermoset polyesters like unsaturated polyester resins used in composites
- Textile polyesters (often simply called “polyester”) typically refer to PET fibers






