The oil and gas sector demands precision-engineered chemistries that synchronize operational throughput with environmental stewardship. Polylactic Acid (PLA) resins function as pivotal thermoplastic aliphatic polyesters, engineered specifically to navigate the complexities of hydraulic fracturing and acidizing. Unlike legacy diverting agents, our PLA grades offer a controlled, hydrolytic degradation profile, facilitating temporary isolation without the risk of long-term formation damage.
Molecular Architecture and Degradation Principles
PLA temporary plugging agents function as high-performance biopolymers providing transient mechanical isolation within complex reservoir architectures. Our resin portfolio is synthesized through the polymerization of high-grade lactide derived from renewable carbohydrate sources, ensuring zero residual formation damage post-operation.
Functional Mechanism
Mechanical Bridging
Granular or powder-form PLA achieves structural bridging through particle size distribution (PSD) optimization. It constructs a low-permeability filter cake at the fracture mouth, sustaining high differential pressures to divert fluid into low-permeability zones.
Self-Mitigating Hydrolysis
Degradation is governed by internal molecular cleavage. Water molecules initiate the breakdown of ester linkages, transitioning the solid polymer into soluble oligomers and ultimately into aqueous lactic acid, eliminating the need for mechanical retrieval.
Degradation Kinetics
we calibrate temporal stability via two primary molecular levers:
- Thermal Response: Hydrolytic cleavage follows a predictable Arrhenius relationship. Higher bottomhole temperatures (BHT) accelerate the polymer’s half-life.
- Stereochemical Tuning: The L-lactide to D-lactide ratio dictates the crystalline-to-amorphous morphology. Our high-crystallinity grades extend structural integrity for HPHT environments, while amorphous grades prioritize rapid dissolution.
Need Expert Guidance on PLA Selection?
Choosing the right PLA resin requires more than just a chemical order; it requires a technical partnership. Our technical team can help determine the optimal PLA formulation for your specific reservoir conditions and completion design through:
- Quality Assurance: We provide resins with consistent L/D ratios to ensure predictable, residue-free degradation kinetics.
- Supply Chain Integrity: All PLA is shipped in hermetically sealed, moisture-controlled packaging to maintain material integrity from our warehouse to your wellhead.
- Engineering Support: Our team assists in analyzing bottomhole temperatures (BHT) and fluid chemistry to recommend the optimal multi-modal PSD formulation.
Main Types of PLA Temporary Plugging Agents
PLA temporary plugging agents are synthesized into distinct geometric configurations—particles, powders, and fibers—each engineered to target specific reservoir topologies and hydraulic requirements.
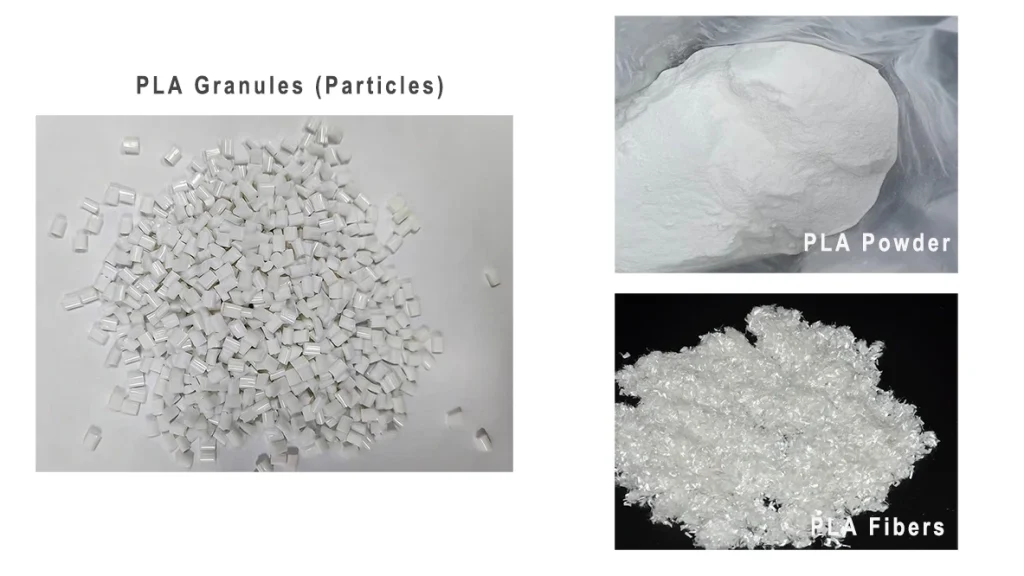

PLA Granules (Particles): Near-Wellbore Structural Integrity
PLA granules are the primary choice for high-pressure diversion within the near-wellbore region.
Characteristics
- Diameter 1.0–4.0 mm
- Compressive strength ≥ 80 MPa
- Specific gravity 1.25.
Function
Forms a robust mechanical bridge across perforations and high-conductivity fractures.
Applications
Cluster isolation in multi-stage fracturing and temporary water-shutoff.

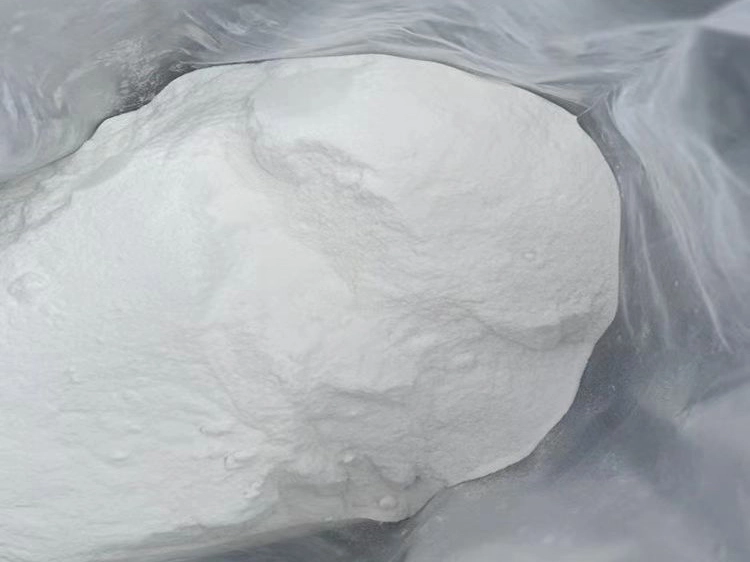
PLA Powder: Matrix Leak-off and Micro-fracture Mitigation
PLA powder provides finer, more uniform diversion capabilities for addressing micro-fractures and high-permeability streaks in the formation.
Characteristics
- Particle size < 150 μm (100 mesh)
- High surface-to-volume ratio for accelerated hydrolytic onset.

Function
Enables the formation of ultra-thin, low-permeability filter cakes to protect the reservoir matrix.
Applications
Far-field diversion and as a supplementary filler in multi-modal diversion systems.
PLA Fibers: Network Reinforcement and Proppant Transport
PLA fibers utilize high aspect ratios to create intricate, three-dimensional interlocking networks.
Characteristics
- Length 3–12 mm
- Diameter 15–40 μm
- High tensile modulus.
Mechanism
Beyond simple bridging, these fibers enhance the viscosity of the carrying fluid via entanglement, significantly improving proppant suspension and preventing premature settling in complex fracture geometries.
Applications
Fracture complexity enhancement and proppant flowback control.

| Morphology | Primary Function | Size Range | Application Scenario | Supply Status |
| PLA Granules | Near-Wellbore Sealing | 1.0–4.0 mm | Perforation sealing & cluster isolation | In Stock |
| PLA Powder | Matrix Leak-off Control | < 150 μm | Micro-fracture mitigation & far-field diversion | In Stock |
| PLA Fibers | Network Reinforcement | 3–12 mm (L) | Proppant transport & complex network bridging | Not Supplied |
Performance Evaluation and Influencing Factors
The operational success of PLA temporary plugging agents is predicated on the precise calibration of material properties against specific downhole variables. Evaluating these polymers requires a rigorous analysis of their mechanical resilience and chemical stability.

Key Performance Metrics
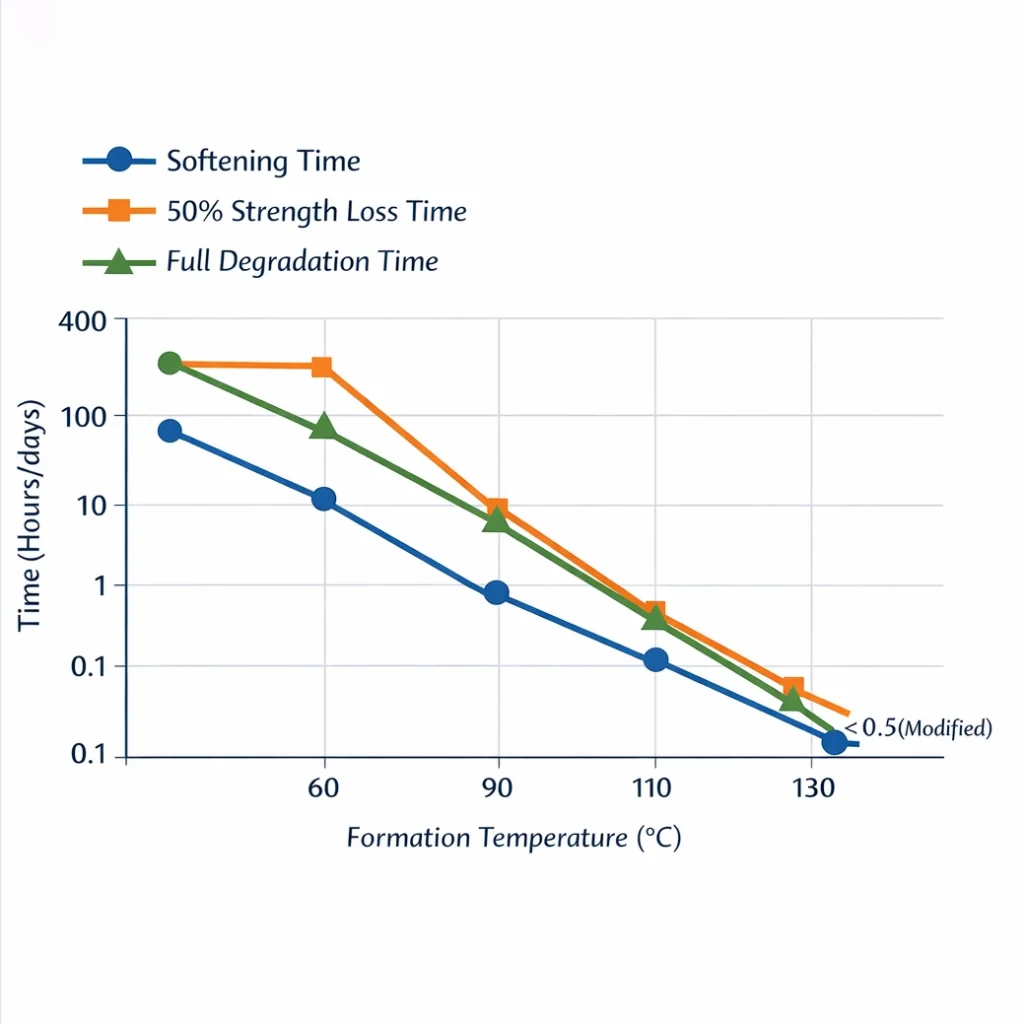
Hydrolytic Window (Degradation Profile)
This defines the temporal boundary between structural integrity and complete dissolution. An ideal PLA grade offers a “latency period” sufficient for stimulation, followed by rapid fragment-free cleanup to restore formation permeability.
Differential Pressure Resistance
Beyond simple compressive strength, this metric assesses the polymer’s ability to resist deformation at elevated temperatures. It is dictated by the material’s Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) and molecular weight (Mw).

Sealing Integrity
Quantified by the pressure response post-injection, this measures the permeability reduction within the target fracture or perforation cluster.

Influencing Factors
Several critical factors influence the performance of PLA temporary plugging agents in downhole environments:
- Thermal Regimes: Bottomhole temperature (BHT) is the primary driver of hydrolysis. For high-temperature reservoirs (> 90°C), high-crystallinity PLA isomers are required to prevent premature softening.
- Aqueous Chemistry: The pH and salinity of the carrier fluid act as catalytic modifiers. Alkaline environments significantly lower the activation energy required for ester bond cleavage, accelerating the degradation timeline.
- Molecular Architecture: As a primary resin supplier, we emphasize that the ratio of L-lactide to D-lactide directly modulates the rate of water diffusion into the polymer matrix, allowing for the engineering of “slow-release” or “rapid-response” plugging agents.
Systems Engineering Approach
Maximizing plugging efficiency necessitates a Multi-Modal Particle Size Distribution (PSD). By integrating high-modulus fibers with optimized granules and micronized powders, operators can achieve an interlocking matrix that minimizes matrix leak-off while ensuring predictable, non-toxic remediation.
Applications, Advantages, and Disadvantages
PLA temporary plugging agents have recalibrated expectations for stimulation efficiency by providing reliable, transient isolation across diverse wellbore environments.
Key Applications
Stage-to-Stage Diversion
In multi-stage hydraulic fracturing, PLA ensures optimized cluster efficiency by facilitating temporary zonal isolation. This maximizes the Stimulated Reservoir Volume (SRV) by diverting fluid into under-stimulated or stress-shadowed zones.
Sealing Lost Circulation Zones
During drilling, PLA serves as an effective bridging agent to mitigate fluid loss in high-permeability or naturally fractured formations, maintaining hydrostatic pressure without permanent pore-throat occlusion.
Refracturing & Re-stimulation
PLA is instrumental in “re-frac” operations to manage pressure depletion. By temporarily shielding depleted parent-well fractures, it forces the initiation of new secondary fractures in virgin rock.
Advantages and Disadvantages
While PLA offers significant operational benefits, its deployment requires a nuanced understanding of its chemical limitations.
Advantages
- 100% autonomous hydrolytic remediation with zero residual skin factor
- Precision-tunable degradation windows via molecular weight and crystallinity calibration
- Full chemical inertness in friction reducers and crosslinked gel systems
- Structural integrity maintenance across 120°F to 350°F thermal gradients
- Carbon-neutral bio-derived feedstock aligning with global ESG mandates
- Rig-time optimization through elimination of high-volume cleanup flushes
Disadvantages
- Higher initial per-unit Capex relative to legacy mineral salts
- Thermal sensitivity requiring specific isomer selection for high-temperature stability
- Hygroscopic material properties necessitating hermetic packaging and moisture control
- Specialized engineering requirements for multi-modal particle size optimization
- Accelerated hydrolysis kinetics in ultra-HT environments exceeding 350°F
Comparative Analysis: PLA vs. Traditional Materials
| Property | PLA Biopolymers | Rock Salt / Benzoic Acid |
| Removal Mechanism | Intrinsic Hydrolysis | Fluid Dilution / Sublimation |
| Formation Damage | Negligible (Total Degradation) | High (Risk of insoluble residue/salinity) |
| Pressure Rating | High (55–85 MPa) | Low to Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Carbon-neutral / Non-toxic | High Salinity / Potential Toxicity |
| Post-op Intervention | None Required | Mechanical Circulation / Flushing |

Optimize Your PLA Performance
Our team can analyze your specific bottomhole temperatures (BHT) and reservoir conditions to recommend the optimal PLA crystallinity and formulation for your project.
Future Developments and Challenges
The trajectory of PLA-based diversion technology is defined by the synthesis of high-performance copolymers and the mitigation of existing geomechanical constraints.

Emerging Innovations
Stimuli-Responsive Degradation
Development of PLA matrices with embedded catalysts or enzymatic triggers to facilitate on-demand dissolution independent of thermal gradients.
Stereocomplex PLA (sc-PLA)
Leveraging the interlocking of PLLA and PDLA chains to elevate the melting point and mechanical modulus for HPHT (High-Pressure High-Temperature) applications.
Nano-Structured Composites
Integration of inorganic reinforcing agents to enhance compressive strength and customize degradation sequences at the molecular level.
Current Technical and Adoption Constraints
HPHT Stability Thresholds
Engineering aliphatic polyesters that maintain structural integrity in ultra-deep reservoirs exceeding 350°F (177°C).
Quantifiable Field Benchmarks
Establishing standardized laboratory protocols (e.g., modified API testing) to minimize performance variance across fluctuating salinity and pH profiles.
CAPEX vs. OPEX Rebalancing
Transitioning the industry perspective from initial procurement costs to total life-cycle savings, including reduced water usage and eliminated mechanical interventions.
Implementation Knowledge Gap
Bridging the technical divide between raw material specifications and real-time downhole diversion design through advanced simulation modeling.
The ESG Integration Driver
The global transition toward decarbonization is recalibrating procurement priorities within the energy sector. PLA temporary plugging agents act as a critical ESG lever, allowing operators to substitute persistent synthetic polymers with bio-derived, carbon-neutral alternatives. This shift facilitates measurable reductions in the environmental footprint of stimulation operations while simultaneously enhancing reservoir recovery efficiency.
Stay Ahead with Advanced PLA Technology
Connect with our research team to learn about the latest developments in PLA temporary plugging technology and how they can benefit your operations.
Conclusion
PLA temporary plugging agents represent a strategic alignment of polymer science and reservoir engineering, addressing the critical requirement for high-integrity isolation followed by autonomous remediation. By leveraging engineered hydrolytic degradation, these materials bridge the gap between aggressive stimulation objectives and the imperative for zero-residual formation protection. This technical synergy ensures that complex fracturing and re-stimulation operations can be executed with maximum cluster efficiency without compromising long-term permeability.
The ongoing evolution of PLA—characterized by enhanced thermal stability and precise kinetic tailoring—reaffirms its role as a fundamental component in the modern completion toolkit. As operators transition toward more carbon-conscious and operationally lean methodologies, the adoption of bio-derived polyesters provides a quantifiable pathway to optimize Stimulated Reservoir Volume (SRV) while adhering to stringent environmental mandates. Ultimately, the integration of advanced PLA grades facilitates a more resilient approach to resource recovery, ensuring that today’s stimulation enhancements do not become tomorrow’s production barriers.


