
Sustainable food packaging starts with precise polymer selection. Forward-thinking food brands are aggressively phasing out conventional plastics, shifting the burden to manufacturers to find viable, bio-based alternatives. This transition presents a critical technical challenge: adopting sustainable materials without compromising production efficiency or consumer safety.
Food Grade PLA (Polylactic Acid) has emerged as the premier resin solution to meet these demands. However, material quality varies significantly across the supply chain. In an era of tightening transparency and certification requirements, selecting the right high-purity feedstock is no longer optional—it is a competitive necessity. This guide examines the technical advantages of premium PLA resins, the current regulatory landscape, and how manufacturers can leverage certified biopolymers to secure their lead in the future of packaging.
Start your transition to high-quality Food Grade PLA today.
Speak with our polymer specialists to identify the ideal resin grade for your specific food contact requirements.
What Is Food Grade PLA?
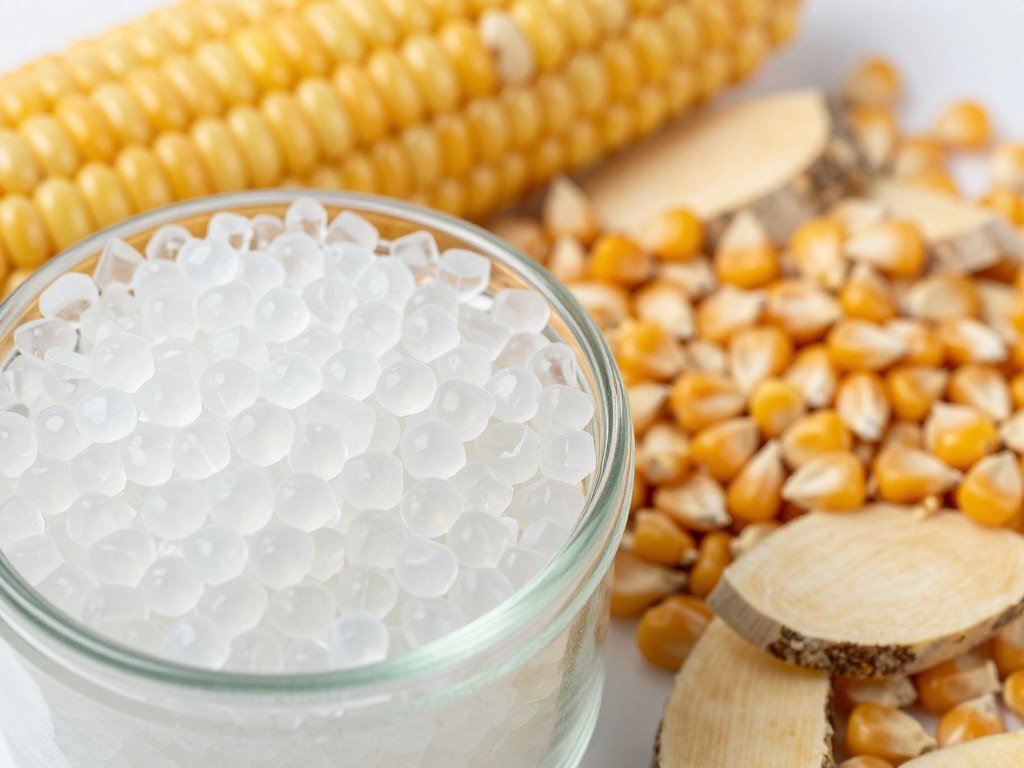

Food Grade Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a high-purity biopolymer resin engineered specifically for the rigorous demands of the food packaging industry. Derived from 100% renewable feedstocks such as cornstarch or sugarcane, this thermoplastic is not merely an eco-friendly substitute—it is a sophisticated material produced through the controlled fermentation of plant sugars into lactic acid, followed by high-vacuum polymerization.
The “Food Grade” designation signifies uncompromising safety and traceability. Our PLA resins are rigorously tested to meet and exceed global food-contact standards, including FDA (US), EU 10/2011 (Europe), and GB (China) regulations. Beyond being free from BPA and phthalates, our food-grade grades ensure that migration levels remain well below legal limits, even under challenging storage conditions.
Technical Advantages for Manufacturers:
- Optimized Melt Flow: Engineered for high-speed processing on conventional extrusion, thermoforming, and injection molding lines.
- High Optical Clarity: Delivers a premium, crystal-clear finish that enhances product visibility on retail shelves.
- Batch Consistency: Strict quality control during polymerization ensures uniform resin properties, reducing downtime and scrap rates for converters.
- Versatile Grades: Available in specialized formulations for various applications, from cold-fill containers to heat-resistant crystalline PLA (CPLA) variants.
Transitioning to our Food Grade PLA allows producers to maintain industrial-scale efficiency while meeting the market’s urgent call for compostable and renewable packaging solutions.
Why Food Grade PLA Matters for Food Packaging

Uncompromising Safety & Market Compliance
Unlike conventional polymers that may leach stabilizers or plasticizers, our Food Grade PLA is inherently inert and non-toxic. It provides a clean, BPA-free barrier that maintains the original taste and aroma of food products. For manufacturers, this resin ensures seamless compliance with the EU Plastic Tax and global food-contact directives, effectively eliminating the risk of regulatory fines or product recalls.
The Balance of Performance and Transparency
Beyond its safety profile, Food Grade PLA delivers high optical clarity and a glossy finish that rivals PET, making it the premier choice for premium retail displays. While standard PLA is ideal for cold-fill applications (up to 50-60°C), our range includes modified CPLA options that extend heat resistance to 90°C for broader versatility.

Strategic Comparison: PLA vs. Traditional Polymers
Understanding how PLA stacks up against conventional resins like PET and PP is crucial for selecting the right material for your production line:
| Performance Metric | Food Grade PLA | Conventional PET / PP |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent (Crystal Clear) | Excellent to Good |
| Heat Resistance | 50–90°C (Grade Dependent) | 100°C+ |
| Sustainability | Compostable & Renewable | Non-Biodegradable |
| Carbon Footprint | Low (LCA Optimized) | High (Fossil-Based) |
| Regulatory Risk | Low (Future-Proof) | Increasing Restrictions |
Operational Future-Proofing through Data
The transition to PLA is a direct response to the global demand for decarbonization. According to Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) data, PLA production generates approximately 60% less greenhouse gas emissions compared to PET. By sourcing our certified compostable feedstock, manufacturers can provide their clients with documented environmental savings, transforming packaging from a mere cost center into a core brand value.
Performance of Food Grade PLA in Food Packaging Applications

Barrier Properties: Protection Where It Counts
Food Grade PLA offers excellent barrier properties for many food packaging applications. It provides good resistance to grease and oils, making it suitable for fatty food products. While its moisture barrier properties are moderate compared to some conventional plastics, they are sufficient for many dry and semi-dry food applications.
For oxygen barrier properties, Food Grade PLA performs adequately for short to medium shelf-life products. For applications requiring enhanced barrier performance, coextruded or laminated structures incorporating PLA can provide additional protection while maintaining the material’s sustainability benefits.

Clarity & Aesthetics: Showcasing Your Products
One of Food Grade PLA’s standout features is its exceptional clarity and glossy finish, rivaling that of PET. This optical quality allows for excellent product visibility, enhancing shelf appeal and allowing brands to showcase their products effectively. The material’s natural shine gives packaging a premium look without requiring additional treatments or coatings.

Rigidity & Strength: Structural Integrity
Food Grade PLA offers excellent rigidity and structural integrity, making it particularly well-suited for thermoformed containers, cups, and trays. Its natural stiffness provides good stack strength for storage and transportation. While it has lower impact resistance than some conventional plastics, formulation adjustments and design considerations can address this limitation for most applications.
Printability & Customization: Brand Expression

Food Grade PLA accepts printing exceptionally well, allowing for vibrant graphics and clear branding. It’s compatible with various printing technologies, including flexographic and digital printing, giving brands flexibility in their packaging design. The material’s surface energy is ideal for ink adhesion, resulting in durable print quality that resists scratching and fading.
Additionally, Food Grade PLA can be easily colored during processing, offering brands the option to create custom-colored packaging without sacrificing the material’s food-safe properties or sustainability benefits. This versatility in customization helps brands maintain their visual identity while transitioning to more sustainable packaging solutions.
| Property | Food Grade PLA | PET | PS | PP |
| Clarity | Excellent | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Rigidity | High | High | Medium | Medium |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate (55-60°C) | Good (70-80°C) | Poor (70-80°C) | Good (100-120°C) |
| Oil/Grease Resistance | Good | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
| Biodegradability | Yes (industrial composting) | No | No | No |
| Printability | Excellent | Good | Good | Fair (requires treatment) |
Most Common Food Packaging Applications for Food Grade PLA

Drink Cups & Straws
Food Grade PLA is ideal for cold beverage containers, offering excellent clarity that showcases the drink while providing sufficient rigidity. Major coffee chains and quick-service restaurants have already adopted PLA cups and straws as part of their sustainability initiatives, with positive customer feedback on performance and environmental benefits.

Takeaway Containers
The rigidity and clarity of Food Grade PLA make it perfect for takeaway food containers and clamshells. These applications benefit from the material’s structural integrity and resistance to oils and fats. Leading food service providers report that PLA containers maintain food freshness while supporting their sustainability messaging.
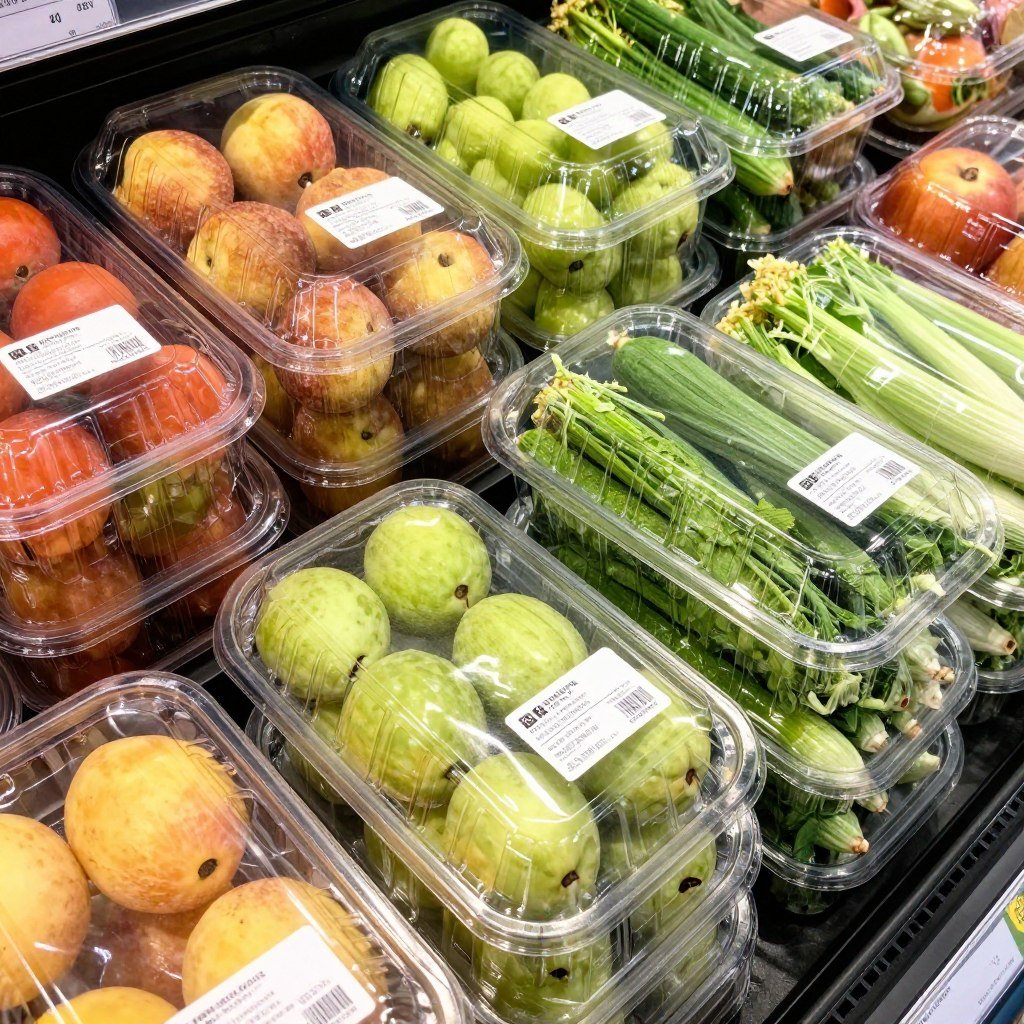

Fresh Produce Packaging
For fresh fruits and vegetables, Food Grade PLA trays and containers offer an excellent balance of protection and presentation. The material’s breathability can be advantageous for certain produce items, potentially extending shelf life while providing sustainable packaging that aligns with the natural positioning of fresh foods.

Bottles & Beverage Containers
Food Grade PLA is increasingly used for water bottles and other cold beverages. While not suitable for carbonated drinks due to gas permeability, it performs well for still beverages and dairy products. Several beverage brands have launched PLA bottles as limited editions or for specific product lines targeting environmentally conscious consumers.
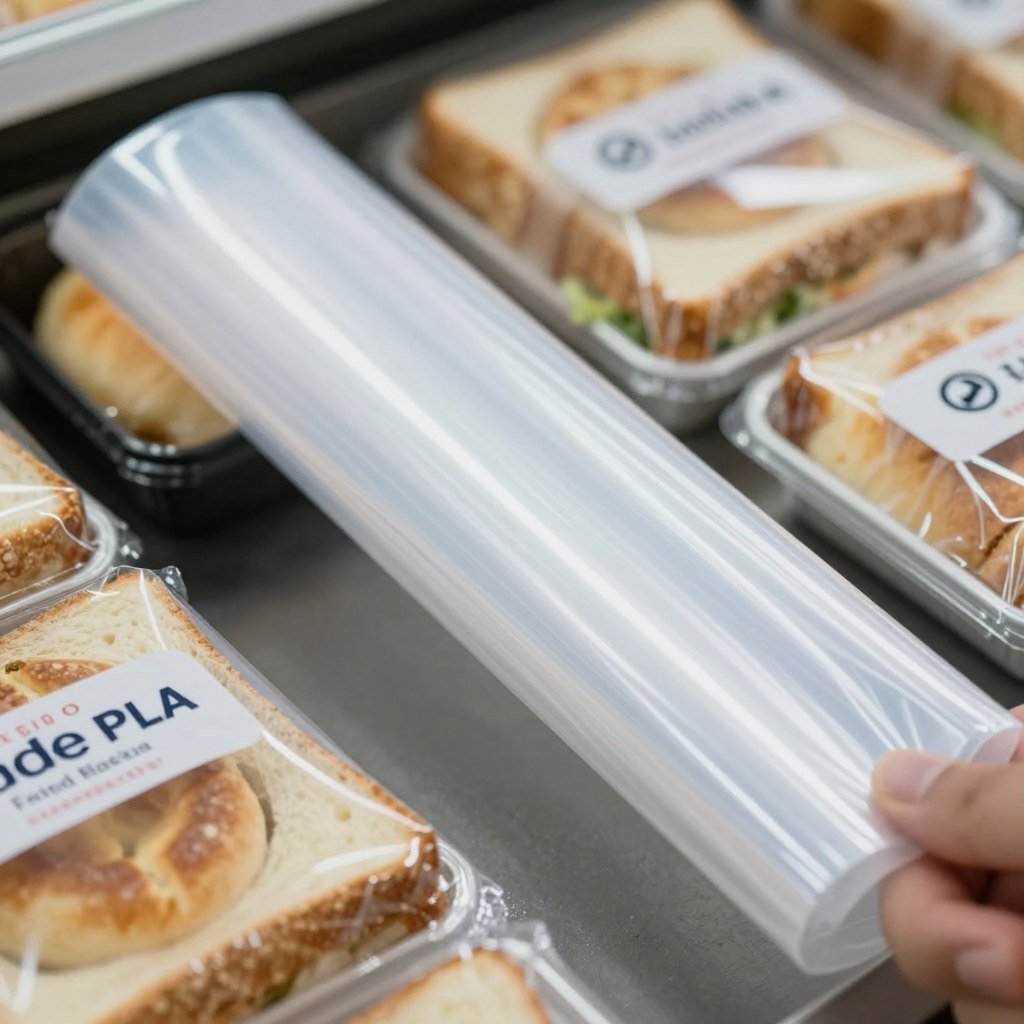

Films & Wrappers
Flexible Food Grade PLA films are suitable for wrapping sandwiches, baked goods, and other food items with short shelf lives. These applications benefit from the material’s breathability and natural feel. Bakeries and sandwich shops report that PLA wrappers maintain product freshness while enhancing their sustainability credentials.

Cutlery & Serving Items
Food Grade PLA cutlery offers sufficient rigidity for single-use applications while providing a more sustainable alternative to conventional plastic utensils. As regulations increasingly target single-use plastics, PLA cutlery provides a compliant solution that maintains functionality. Food service providers report high customer satisfaction with PLA utensils.
“Our transition to Food Grade PLA packaging has not only helped us meet our sustainability goals but has also resonated strongly with our customers. The material performs exceptionally well for our fresh produce line, and we’ve seen increased engagement from environmentally conscious consumers.”
— Sarah Chen, Packaging Innovation Director, GreenHarvest Foods
Cost Comparison: Food Grade PLA vs Traditional Plastics
When evaluating the economics of Food Grade PLA against traditional plastics, it’s important to consider both direct costs and the total cost of ownership. Currently, the raw material cost of Food Grade PLA is typically 20-30% higher than conventional plastics like PET or PS. However, this gap continues to narrow as production scales increase and more manufacturers enter the market.
Direct Cost Considerations
The processing of Food Grade PLA can be accomplished using existing plastic manufacturing equipment with minimal modifications, reducing transition costs. Energy consumption during processing is often lower than with conventional plastics due to PLA’s lower melting temperature, potentially offsetting some of the higher material costs through reduced energy expenses.
For companies already using PET or similar materials, the switch to Food Grade PLA typically requires minimal capital investment, making the transition more economically feasible than other alternative materials that might require completely new processing equipment.
Total Cost of Ownership
Beyond direct material costs, Food Grade PLA offers several economic advantages that impact the total cost of ownership. As regulations on conventional plastics tighten, compliance costs for traditional materials are likely to increase, while sustainable alternatives like PLA may avoid these additional expenses.
Many brands report being able to command premium pricing for products packaged in sustainable materials, with consumers willing to pay 5-10% more for products with environmentally friendly packaging. This price premium can offset the higher material costs while enhancing brand value and customer loyalty.
Cost Optimization Strategies for Food Grade PLA:
- Optimize design to reduce material usage while maintaining performance
- Consolidate purchasing to leverage volume discounts
- Explore tax incentives and subsidies available for sustainable packaging
- Highlight sustainability in marketing to capture price premiums
- Consider the long-term cost avoidance of regulatory compliance issues
As production volumes increase and technology advances, the cost gap between Food Grade PLA and conventional plastics is expected to continue narrowing. Forward-thinking companies recognize that early adoption positions them advantageously as the market shifts toward sustainable solutions, potentially avoiding costly rapid transitions in the future as regulations tighten.
How to Choose a Reliable Food Grade PLA Supplier

Selecting the right Food Grade PLA supplier is crucial for ensuring consistent quality, regulatory compliance, and reliable supply. As the market for bioplastics expands, it’s important to evaluate potential suppliers thoroughly to establish a partnership that supports your packaging needs and sustainability goals.
Essential Certifications & Compliance

Verify that your supplier provides Food Grade PLA with proper certifications for food contact applications. Look for:
- FDA compliance documentation (21 CFR 175.300 or equivalent)
- EU compliance with Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 and Regulation (EU) No 10/2011
- Biodegradability certifications (ASTM D6400, EN 13432)
- ISO 9001 quality management certification
- Migration testing results for specific food types
Quality & Consistency
Consistent material properties are essential for efficient processing and reliable packaging performance. Evaluate suppliers based on:
- Batch-to-batch consistency in melt flow rate and mechanical properties
- Quality control processes and testing frequency
- Clarity and color consistency across production runs
- Documented quality assurance procedures
- Track record with similar applications in the food industry
Technical Support & Expertise
The transition to Food Grade PLA may require technical adjustments to your manufacturing process. A valuable supplier should offer:
- Processing guidelines specific to your equipment
- Technical support for troubleshooting and optimization
- Application development assistance
- Knowledge of food packaging regulations and requirements
- Resources for educating your team on bioplastic handling
Supply Chain Reliability
Ensure your supplier can meet your volume requirements consistently:
- Production capacity aligned with your needs
- Multiple manufacturing facilities for supply redundancy
- Inventory management practices
- Transparent lead times and delivery reliability
- Contingency plans for supply disruptions
Sustainability Credentials

A truly sustainable supplier should demonstrate commitment beyond just providing a biodegradable product:
- Transparent sourcing of raw materials (non-GMO options if required)
- Documentation of carbon footprint and life cycle assessment
- Sustainable manufacturing practices and renewable energy use
- Responsible water management and waste reduction initiatives
- Third-party sustainability certifications
Red Flags When Evaluating Food Grade PLA Suppliers:
- Inability to provide proper food contact certifications
- Vague or unsubstantiated claims about material properties
- Lack of technical data sheets or safety documentation
- No established quality control procedures
- Unwillingness to provide samples for testing
Building a strong relationship with your Food Grade PLA supplier is an investment in your product quality and brand reputation. Take time to thoroughly evaluate potential partners, request samples for testing in your specific applications, and establish clear expectations for ongoing support and collaboration.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Food Packaging

Food Grade PLA represents a significant advancement in sustainable food packaging, offering a compelling combination of safety, performance, and environmental benefits. As consumer preferences continue to shift toward eco-friendly options and regulations increasingly target conventional plastics, PLA provides a proactive solution that addresses current challenges while positioning brands for future success.
The material’s versatility across various food packaging applications—from rigid containers to flexible films—makes it adaptable to diverse product needs. While the initial material cost may be higher than conventional plastics, the total value proposition, including brand enhancement, regulatory compliance, and consumer preference, makes Food Grade PLA an increasingly attractive option for forward-thinking food brands and manufacturers.
As production scales increase and technology advances, we can expect continued improvements in both performance and economics, further strengthening the case for adoption. Companies that begin transitioning to Food Grade PLA now will gain valuable experience and market positioning as the industry continues its shift toward sustainable packaging solutions.
Ready to transform your food packaging?
Our team of packaging experts can help you evaluate Food Grade PLA for your specific applications and develop a transition strategy that aligns with your business goals.
Is Food Grade PLA suitable for hot foods and beverages?
Food Grade PLA has a heat deflection temperature of approximately 55-60°C (131-140°F), making it suitable for cold to warm applications but not for hot foods or beverages above this temperature range. For hot food applications, consider PLA-based composites with enhanced heat resistance or other bioplastic alternatives.
How does Food Grade PLA compare to PET for shelf life?
Food Grade PLA generally offers moderate barrier properties compared to PET, making it most suitable for products with short to medium shelf lives. For products requiring extended shelf life, PLA can be used in multi-layer structures or with barrier coatings to enhance performance while maintaining sustainability benefits.
What end-of-life options exist for Food Grade PLA packaging?
Food Grade PLA is industrially compostable according to standards like ASTM D6400 and EN 13432, breaking down into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass under controlled conditions. While not suitable for home composting, it can be processed in industrial composting facilities. As infrastructure develops, this provides a circular end-of-life option not available for conventional plastics.


