The integration of medical-grade Polylactic Acid (PLA) has established it as a decisive polymer within high-performance healthcare applications. This biocompatible and renewable thermoplastic is highly valued for its inherent mechanical strength, predictable hydrolytic degradation profiles, and adaptability across diverse medical device formats, from resorbable sutures to complex orthopedic fixtures. However, material procurement demands a meticulous specification process. Success hinges on expertly balancing demanding regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, ISO standards) with the precise stereochemical structure and molecular weight needed to meet specific application kinetics. This paper provides a granular analysis of the performance metrics and distinct grade differentiations of medical PLA, serving as a critical resource for advanced material evaluation.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance Standards
The deployment of medical-grade PLA mandates a thorough adherence to global regulatory frameworks, positioning compliance as the foremost risk mitigation factor in the material supply chain. For manufacturers, verifying a supplier’s knowledge and documentation capabilities is non-negotiable.
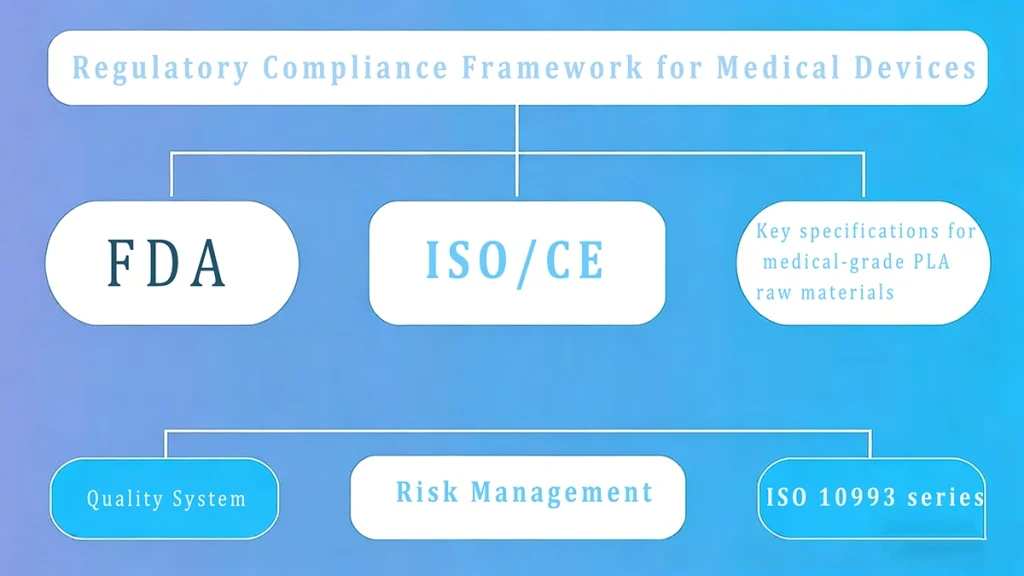
Figure 1: Regulatory framework for medical-grade PLA in healthcare applications
Global Regulatory Benchmarks
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifies PLA-based devices primarily under Class II or III, which dictates the required submission pathway. Critical to all device classes, especially for novel materials, is adherence to the Quality System Regulation (QSR) , ensuring stringent manufacturing process control.
| FDA Classification | Primary Regulatory Action | Key Requirements |
| Class I (Low Risk) | Mostly 510(k) Exempt | General Controls, QSR Compliance |
| Class II (Moderate Risk) | 510(k) Premarket Notification | Substantial Equivalence, Biocompatibility Data |
| Class III (High Risk) | Premarket Approval (PMA) | Clinical Trials, Comprehensive Safety & Efficacy Data |
Internationally, the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) also imposes rigorous requirements, specifically demanding enhanced Post-Market Surveillance (PMS) for all materials used in devices.
Core Material Standards
The biological safety of PLA is confirmed via ISO 10993 standards, which evaluate the material’s interaction with the body based on the contact duration. Essential tests include:
- ISO 10993-5: Cytotoxicity (Cellular Response)
- ISO 10993-10: Irritation and Sensitization
- ISO 10993-11/6: Systemic Toxicity and Implantation Testing
Furthermore, the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Class VI certification signifies a material’s suitability for high-risk applications, relying on systemic injection and implantation studies to confirm minimal biological reactivity.
Classification of Medical-Grade PLA Types
The functional properties of medical-grade PLA are fundamentally driven by its stereochemical composition, dictating the material’s inherent crystallinity, mechanical strength, and degradation kinetics. For material specification, a systematic classification based on these intrinsic factors and their corresponding processing compatibility is essential.
Core Stereochemical Classifications
- PLLA (Poly-L-Lactide): Highly crystalline and strong, offering slower degradation profiles. Predominantly used for long-term implantable devices (e.g., orthopedic fixation).
- PDLA (Poly-D-Lactide): Exhibits properties similar to PLLA. Often co-crystallized with PLLA to form stereocomplex PLA (sc-PLA), significantly enhancing thermal stability and mechanical performance.
- PDLLA (Poly-D,L-Lactide): Amorphous with no defined crystal structure, leading to faster, more homogeneous degradation. Preferred for drug delivery systems and short-term applications.
This structural foundation is critical, as it directly translates into the practical processing parameters used by commercial suppliers. For a comprehensive overview of how manufacturers like NatureWorks define their grades, including the technical specifications for Melt Flow Index (MFI), D-Lactic Acid Content, and Molecular Weight (Mw) tailored for injection, extrusion, and fiber applications, readers are encouraged to consult our specialized guide:《PLA Material: NatureWorks Injection, Extrusion & Fiber Grades》.
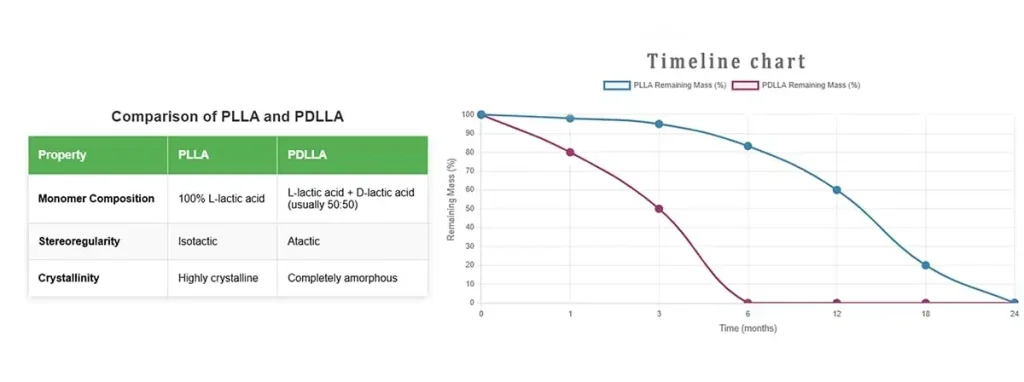
Figure 2: Comparison of PLLA and PDLLA Structural characteristics and degradation time.
Processing-Optimized Grades and Applications
Raw PLA resin is further tailored via molecular weight adjustment to optimize its performance across various fabrication methods.
Injection Molding Grade
These grades feature tightly controlled Melt Flow Rate (MFR) and thermal stability for high-volume manufacturing of precision components.
Advantages
- Flow Properties:High flow rates (MFR ≈ 10-25 g/10min)
- Dimensional Stability:Low mold shrinkage
- Drying Requirement:Residual moisture content ≤ 200 ppm
Limitations
- Minimizes shear heating and molecular weight reduction during filling.
- Essential for precision medical instruments and complex drug delivery housings.
- Prevents hydrolysis during high-temperature processing.
Key Applications
- Precision instruments
- Drug delivery devices
- Non-load-bearing implantable components
Fiber/Extrusion Grade
Optimized for melt spinning and mono- or multifilament extrusion, these formulations require high molecular weights to achieve the necessary draw ratio for tensile strength.
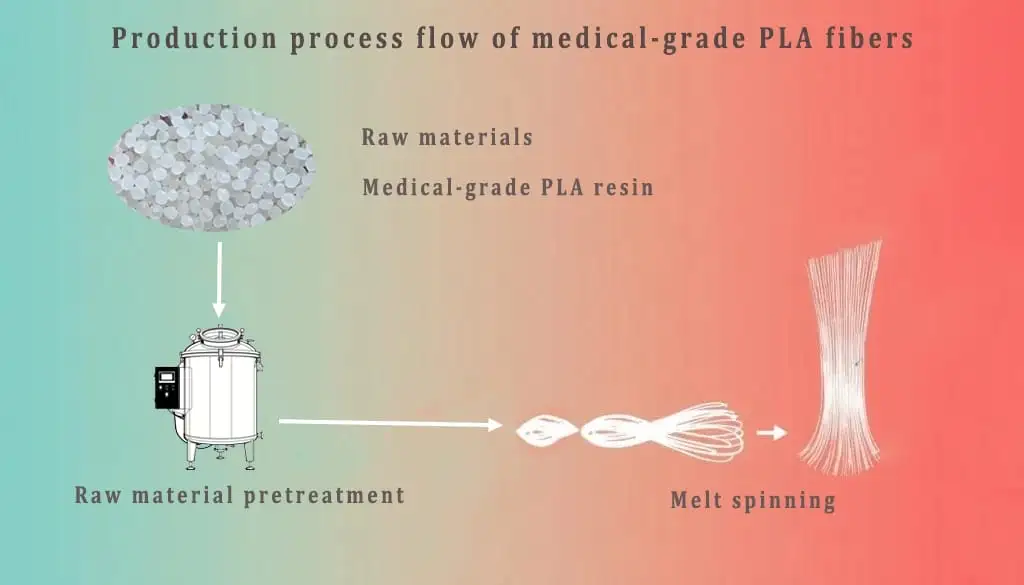
Figure 3: Medical PLA fiber production process
Processing Parameters
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Performance Impact |
| Melt Spinning Temperature | 220-245°C | Affects thermal decomposition and molecular orientation. |
| Draw Ratio | 4:1 to 8:1 | Directly correlates to maximum tensile strength and modulus. |
| Annealing Temperature | 70-90°C | Controls the final degree of crystallinity and degradation rate. |
Key Applications
- Absorbable sutures
- Nonwoven textile scaffolds
- Sterile wound dressings
3D Printing Grade
Grades designed for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) require specific rheological properties to ensure layer adhesion without nozzle clogging.
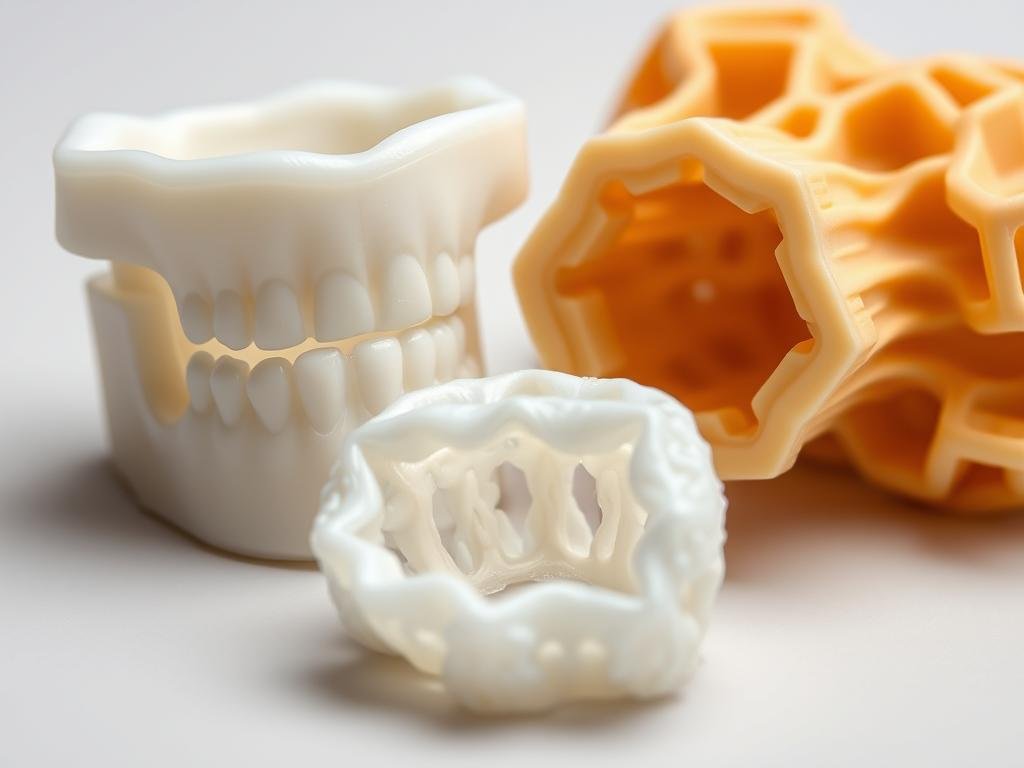
Figure 4: 3D printed medical-grade PLA implant and scaffold structures
Printing Parameters
| Parameter | FDM PLA (Typical) | SLA PLA (Resin) |
| Extrusion Temp. | 195-215°C | N/A (Photopolymerization) |
| Layer Height | 0.1-0.2 mm | ≤ 0.1 mm (High resolution) |
| Build Plate Temp. | 50-65°C | Ambient or 25-35℃ |
Key Applications
- Patient-specific implants
- Custom surgical guides
- Anatomical models
Film/Sheet Grade
Formulations targeting thin-gauge applications must balance melt strength (for blown film) with processability (for cast film).
Processing Parameters
| Parameter | Cast Film | Blown Film |
| Extrusion Temperature | 190-210℃ | 180-200℃ |
| Melt Strength | Low-Medium | Medium-High (for bubble stability) |
| Thickness Range | 15-250 μm | 20-100 μm |
Key Applications
- Sterile barrier packaging
- Temporary implant membranes
- Transdermal patches
Find the Right PLA Grade for Your Application
Our material specialists can help you identify the optimal medical-grade PLA formulation based on your specific manufacturing process and application requirements.
Recommended Mainstream Medical-Grade PLA Products
Material selection necessitates reliance on well-documented polymers with proven clinical history and robust regulatory support packages. The following sections provide a technical overview of established medical-grade Polylactide (PLA) and related polylactide copolymer solutions, emphasizing key performance indicators (KPIs) critical for device design.

Figure 5: Medical-grade PLA pellets from leading manufacturers
NatureWorks Ingeo™ Medical Series
NatureWorks offers a comprehensive range of medical-grade PLA under the Ingeo™ brand, with formulations optimized for different processing methods and applications.
Ingeo™ 3100HP
A high-performance injection molding grade with excellent flow properties and dimensional stability, suitable for precision medical components.
- Melt Flow Rate: 24 g/10 min (210°C/2.16 kg)
- Tensile Strength: 65 MPa
- Processing Focus:High-Precision Injection Molding
- Regulatory: FDA food contact, USP Class VI
Ingeo™ 3D850
Optimized for 3D printing applications, offering excellent layer adhesion and dimensional stability for medical prototypes and custom devices.
- Flexural Modulus: 2.5 GPa
- Print Temperature Range: 190-220°C
- Processing Focus:Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Regulatory: FDA food contact
Ingeo™ 6500D
Specifically designed for fiber applications, this grade offers excellent melt strength and drawability for medical sutures and nonwoven fabrics.
- Melt Flow Rate: 14 g/10 min (210°C/2.16 kg)
- Elongation at Break(post-drawing): 3.5%
- Processing Focus : Fiber and Monofilament Extrusion
- Regulatory: ISO 10993 tested
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Other Well-Known Medical-Grade PLA Brands
| Brand | Grade | Type | Key Features | Primary Applications |
| Evonik | RESOMER LR | L-lactide based | Controlled degradation profiles | Controlled release systems |
| Toray | ECODEAR P-X001 | Film/Sheet | Excellent transparency | Medical packaging |
Comparison of Key Technical Parameters
The table below illustrates the typical mechanical and degradation ranges associated with different PLA processing requirements.
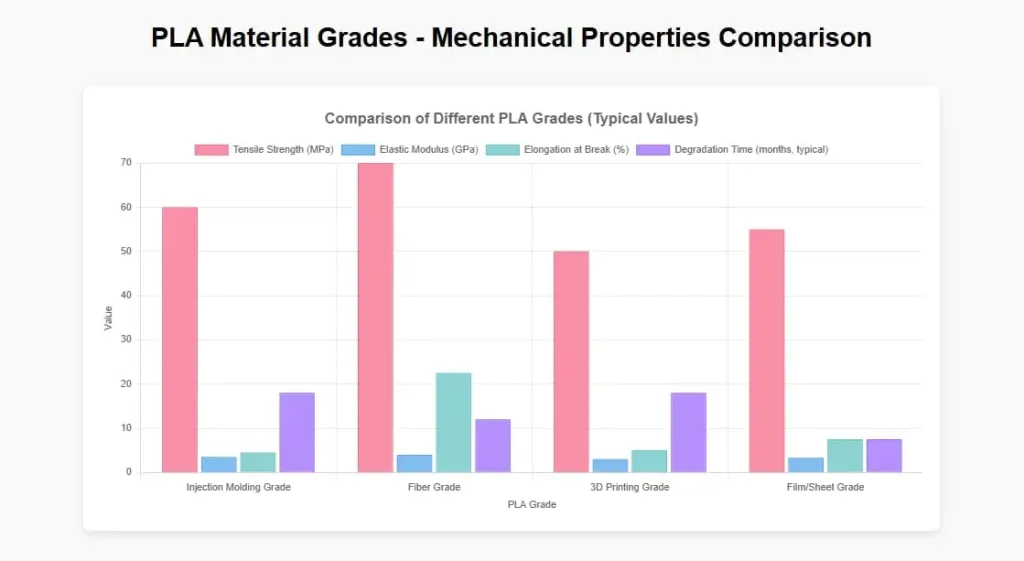
Figure 6: Mechanical property comparison of medical-grade PLA
| Property | Injection Molding Grade | Fiber Grade | 3D Printing Grade | Film/Sheet Grade |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 50-70 | 60-80 | 40-60 | 45-65 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 3.0-4.0 | 3.5-4.5 | 2.5-3.5 | 2.8-3.8 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 3-6 | 15-30 | 3-7 | 5-10 |
| Degradation Time (Typical months) | 12-24 | 6-18 | 12-24 | 3-12 |
Advanced Medical-Grade Polymer Solutions
Medical-grade PLA is available in sophisticated formulations to overcome inherent limitations like brittleness or fixed degradation rates. These advanced solutions typically involve materials pre-compounded or synthesized by the supplier.
Copolymer and Stereocomplex Solutions
- PLA-PGA Copolymers (PLGA): These specialized copolymer grades are synthesized with hydrophilic glycolide (GA) units to accelerate hydrolysis. The PLA:PGA ratio directly controls the degradation rate, allowing manufacturers to select grades ranging from 1 to 18 months for controlled drug delivery.
- Toughened PLA Grades (PLA-PCL): Integrating Polycaprolactone (PCL) into the polymer structure creates tougher, more flexible grades to address PLA’s inherent brittleness, making them suitable for soft tissue applications.
| PLA:PGA Ratio | Degradation Time (Range) | Key Property Profile |
| 85:15 | 5-6 months | Good mechanical strength, moderate degradation |
| 50:50 | 1-2 months | Fastest degradation rate, moderate strength |
Bioactive and Reinforced Grades
Specialized compounded grades incorporate functional fillers to enhance performance and bioactivity:
- Reinforced Grades: Grades containing Hydroxyapatite (HA) are available for osteoconductivity and mechanical reinforcement, crucial for bone tissue engineering applications.
- Functionalized Grades: Certain grades incorporate nanoparticles like Magnesium Oxide (MgO), which can provide antimicrobial activity and buffer the acidic degradation byproducts, enhancing biocompatibility.
Medical-Grade PLA Selection Decision Process
The material selection process for medical-grade PLA must follow a stringent, systematic protocol, treating the choice as a critical design input
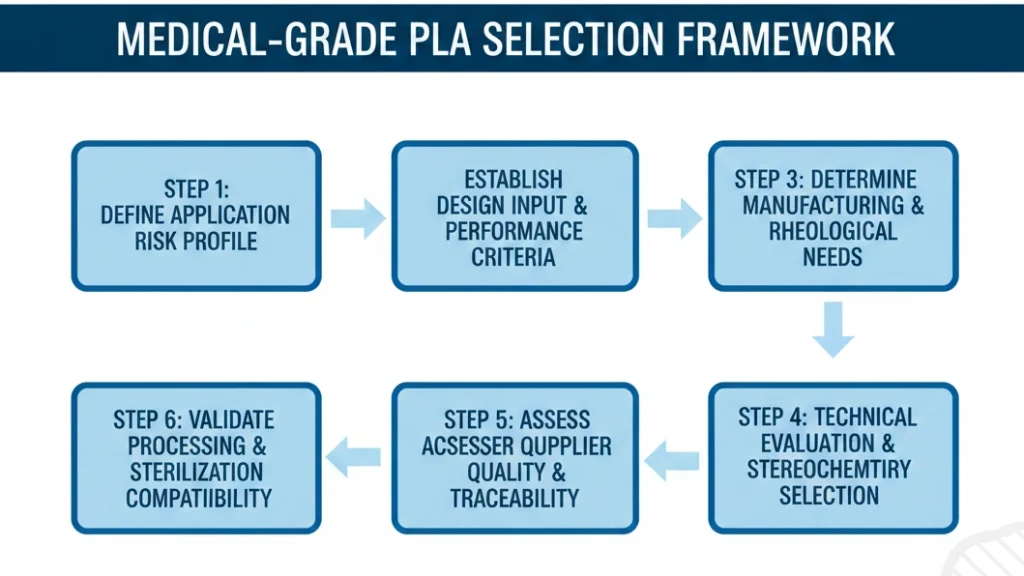
Figure 7: Medical-grade PLA selection decision flowchart
Step 1: Define Application and Risk Profile
- Document the device’s intended use and clinical function.
- Specify the required duration of body contact
- Determine the mandatory FDA classification (Class I, II, or III) to set the regulatory foundation.
- Establish the baseline stringency for ISO 10993 biocompatibility testing.
Step 2: Establish Design Input and Performance Criteria
- Translate clinical needs into quantified metrics for Tensile Modulus and required Fatigue Limit.
- Specify the exact Degradation Timeline for mechanical retention and full absorption.
- Confirm compatibility with the intended sterilization method (EO, Gamma, or E-beam).
Step 3: Determine Manufacturing and Rheological Needs
- Select the primary fabrication method (e.g., injection molding, extrusion, or additive manufacturing).
- Define the necessary rheological properties, such as the required Melt Flow Index (MFI) and thermal stability.
- Assess preliminary material cost versus expected processing yield and tooling complexity.
Step 4: Technical Evaluation and Stereochemistry Selection
- Select the appropriate Stereochemical Composition (PLLA, PDLLA, co-polymer) to align the material’s crystallinity with the required degradation rate.
- Compare supplier data sheets, focusing on physical properties (Crystallinity, Tg).
- Assess the need for modification (e.g., PLGA copolymerization or plasticization) to meet performance gaps.
Step 5: Assess Supplier Quality and Traceability
- Verify the supplier’s adherence to the Quality Management System (QMS) standards.
- Assess the guaranteed batch-to-batch consistency and availability of raw material.
- Request comprehensive Regulatory Support Files and necessary certifications (e.g., USP Class VI).
Step 6: Validate Processing and Sterilization Compatibility
- Confirm the optimal processing window (e.g., drying requirements, melt stability) through prototype trials.
- Validate that the chosen sterilization method does not induce detrimental molecular weight loss or embrittlement in the material.
Finalize Material Documentation and Control
- Formalize the material selection against the supplier’s Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
- Detail all final Processing Parameters and critical quality control points.
- Ensure all supporting data and test reports are archived for future regulatory audits.
PLA Medical Grade Application
The following applications demonstrate how precise polymer selection, customization, and processing can overcome demanding design challenges in the medical field.
Absorbable Bone Screws and Plates

Figure 8: PLA-HA composite bone fixation devices
- Application Focus: High-load orthopedic fixation devices designed for gradual load transfer and eventual full absorption.
- Material Grade Focus: High Molecular Weight PLLA Resin (e.g.,
NatureWorks 3100HPBase) or PLLA-HA Reinforced Grades.
- Key Performance Requirements: Sufficient initial mechanical strength and fatigue resistance; Osteoconductivity; Controlled degradation timeline (12–24 months).
Drug Release Microspheres and Scaffolds
- Application Focus: Microparticles for sustained and localized delivery of pharmaceutical agents.
- Material Grade Focus: L-Lactide-co-Glycolide (PLGA) or Amorphous PDLLA grades optimized for short degradation profiles.
- Key Performance Requirements: Tunable degradation rate directly correlating with drug release kinetics (e.g., 1 to 6 months); High purity and consistent molecular weight for uniform particle formation.
Medical Surgical Sutures and Sterile Dressings
- Application Focus: Extruded filaments requiring high tensile strength and predictable absorption for soft tissue approximation.
- Material Grade Focus:High Molecular Weight Fiber-Grade PLLA Resin (e.g.,
NatureWorks 6500D)
- Key Performance Requirements: High knot security and sufficient initial tensile strength retention (typically 2–3 weeks); Predictable, complete absorption.
- Note: The selected material must be compatible with Ethylene Oxide (EO) sterilization, typically preferred to minimize molecular chain damage.
Ready to Select the Right Medical-Grade PLA?
We provide detailed specifications and application recommendations for our medical-grade PLA products.
Conclusion
The selection of an appropriate medical-grade PLA formulation is a critical decision that directly impacts device performance, regulatory approval, and clinical outcomes. This guide has outlined the essential considerations in the selection process, including regulatory compliance, material classifications, property enhancements, and practical applications.
The landscape of medical PLA materials is rapidly evolving, shifting toward products with significantly enhanced properties. Emerging trends in raw material supply include the commercialization of high-purity sc-PLA grades offering superior thermal performance and the introduction of a wider array of pre-compounded, function-specific resins (e.g., reinforced or plasticized grades) to simplify manufacturing complexity.
By following the systematic selection process outlined in this resource and staying informed about material innovations, medical device manufacturers can leverage the full potential of medical-grade PLA to develop safe, effective, and innovative healthcare solutions.



