The global textile sector has reached a defining structural pivot. As Carbon Neutrality mandates and Sustainable Fashion frameworks transition from voluntary pledges to enforceable regulations, the industry faces a rigorous landscape of Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanisms (CBAM) and stringent green supply chain certifications. For synthetic fiber producers, the era of relying solely on petroleum-based expansion is being superseded by a paradigm that penalizes high-carbon footprints and microplastic liability.
PLA (Polylactic Acid) fiber stands as the most mature, technologically vetted solution to this challenge. It offers a viable pathway for existing infrastructure to transition away from fossil fuels. With a carbon footprint significantly lower than polyester, high-purity PLA resin is no longer a niche alternative; it is the scalable cornerstone for the next generation of low-carbon, circular textiles.
The Environmental Mandate: Why PLA?
The environmental crisis in traditional textiles has evolved from a reputational risk to a financial liability. Petroleum-based synthetics subject global supply chains to the growing volatility of carbon taxes and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) fees.
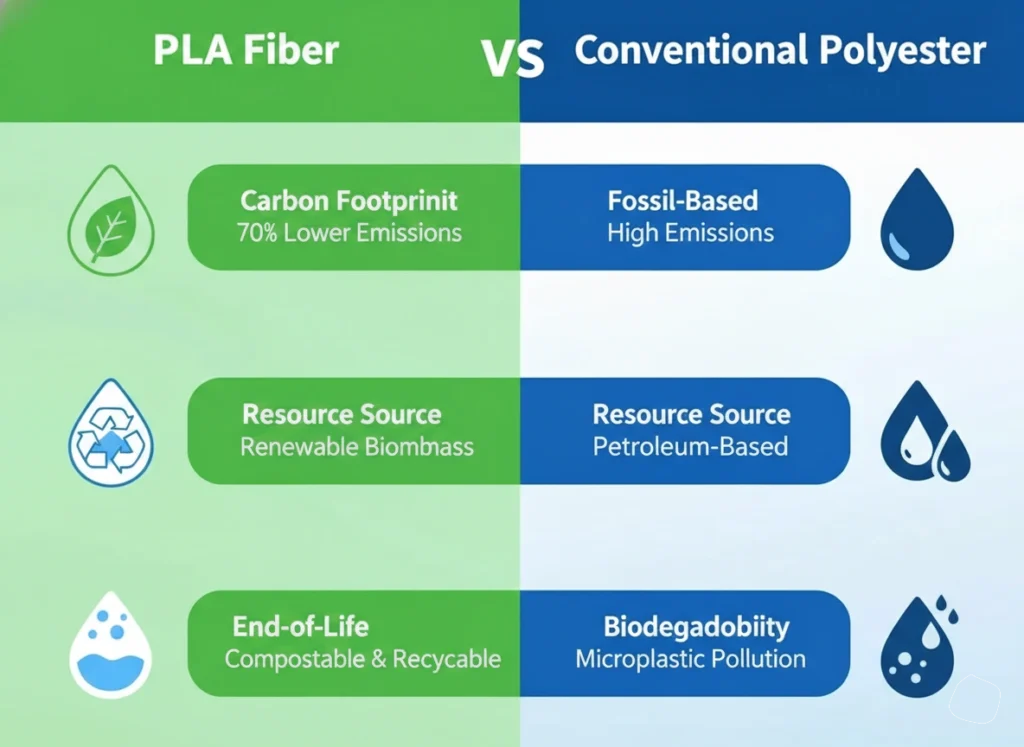
Biodegradable fiber facilitates a strategic decoupling from this carbon-intensive legacy. Synthesized from rapidly renewable biomass, its production (from cradle-to-gate) reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70-80% compared to virgin fossil-based polymers.
Beyond carbon reduction, biodegradable fiber addresses the issue of microplastic persistence.While infrastructure for widespread garment composting is still scaling, PLA’s industrial compostability (meeting EN 13432 / ASTM D6400 standards) serves as a technical validation of its biological compatibility. More importantly, it offers a lower-impact profile in cases of microfiber loss compared to traditional synthetics, helping brands mitigate long-term environmental liability.
Navigating the shift toward carbon-neutral textiles?
Get a comparative LCA analysis and technical data sheets to see how our PLA resins integrate into your existing production lines.
Core Advantages of PLA Fiber
PLA fiber has evolved into a strategic powerhouse that transcends simple environmental compliance. By offering a high-purity, bio-based resin derived from renewable biomass—such as corn, sugarcane, or lignocellulosic straw—it provides a definitive departure from fossil-fuel dependency. While traditional synthetics create persistent microplastic waste, our fiber-grade PLA is engineered for biological circularity. It undergoes mineralization into CO₂ and water under industrial composting conditions,providing a critical end-of-life alternative while significantly lowering the Product Environmental Footprint (PEF) from the outset.
Technical Performance Comparison
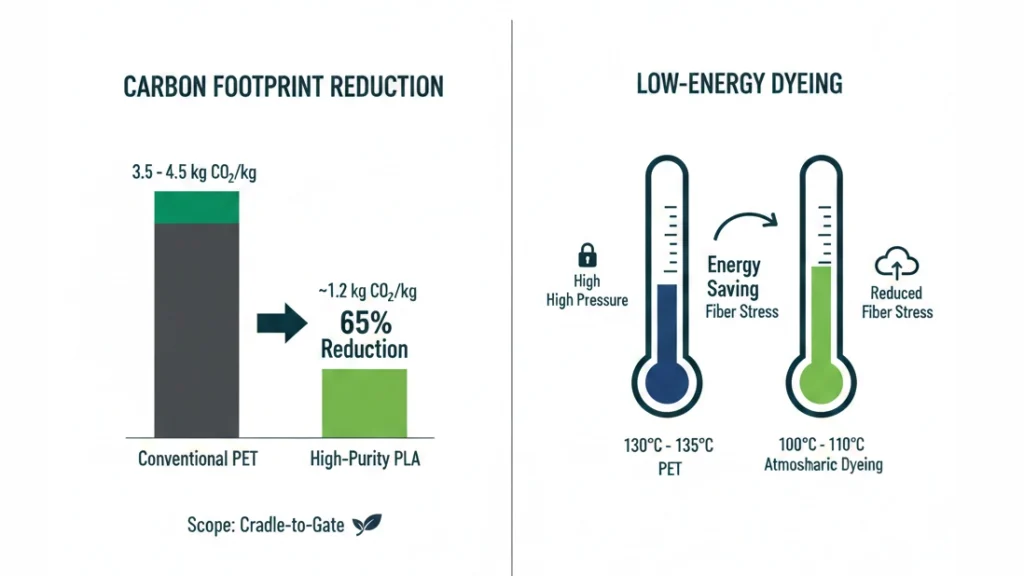
To ensure a successful transition, we benchmark high-grade PLA resins against conventional Synthetic Fibers (PET).
| Property | High-Purity PLA Fiber | Conventional Polyester (PET) | Scientific Advantage |
| Carbon Footprint | ~1.2 kg CO₂/kg | ~3.5 – 4.5 kg CO₂/kg | 65%+ Reduction (Cradle-to-Gate) |
| Moisture Regain | 0.4% – 0.6% | 0.2% – 0.4% | Higher Hydrophilicity (Reduced Cling) |
| Melting Point | 130°C – 170°C | 250°C – 260°C | Energy Saving (Low-Temp Processing) |
| Dyeing Temp | 100°C – 110°C | 130°C – 135°C | Atmospheric Dyeing (No Pressure) |
| Skin Compatibility | Weakly Acidic (pH ~6.0) | Neutral / Inert | Matches Human Skin pH |
| Flammability | LOI 24–26% | LOI 20–22% | Inherent Self-Extinguishing Tendency |
Note: To achieve these performance benchmarks, we utilize high-heat PLA grades or specific melting-point-enhancing additives. This ensures the fiber maintains structural integrity during high-temperature downstream processing, such as heat-setting and finishing.
Industrial Integration and Process Stability
One of the most critical advantages for spinning and non-woven enterprises is the exceptional processability of advanced PLA resins. With a versatile melting point (130–170°C) and superior melt stability, PLA allows for seamless integration into existing melt-spinning infrastructure with minimal retooling. Current modified grades now offer high breaking strength (reaching 4.5–5.0 cN/dtex and above) and optimized elongation, significantly reducing filament breakage and ensuring production efficiency equivalent to conventional polyester.
Functional Differentiation and Consumer Appeal
At the consumer level, biodegradable fiber unlocks a premium sensory experience. Its natural pH of 5.5–6.5 mirrors human skin acidity, making it inherently hypoallergenic and ideal for infant wear and intimate apparel. This skin-friendly profile is complemented by superior moisture-wicking and antimicrobial properties, inhibiting odor-causing bacteria without chemical additives. Furthermore, this material offers a silk-like luster, elegant drape, and enhanced safety through its inherent self-extinguishing flame retardancy—properties that fossil-based alternatives struggle to match.
Optimized Dyeing and Supply Chain Maturity
Transitioning to PLA no longer necessitates compromising on aesthetics or cost. Current PLA fibers exhibit excellent affinity for disperse dyes, achieving vibrant color saturation and high fastness at lower temperatures (90–110°C). This synergy extends to blending with cotton, Lyocell, or Modal, resulting in dimensionally stable, wrinkle-resistant fabrics. As global capacity from industry leaders expands and second-generation feedstock technologies stabilize, the cost gap with virgin polyester continues to narrow, positioning PLA as the most scalable, high-margin solution for the next generation of circular textiles.
Processing & Versatility – From Our PLA Raw Materials to Your Fibers
Bridging the gap between raw bio-polymers and high-grade textiles requires a material that balances environmental integrity with industrial efficiency. Our fiber-grade PLA resins are engineered for high-speed extrusion, offering a technically viable solution for existing polyester and polypropylene infrastructure. By maintaining rigorous control over molecular weight distribution and melt viscosity, these pellets provide the thermal stability essential for complex spinning cycles and consistent filament formation.
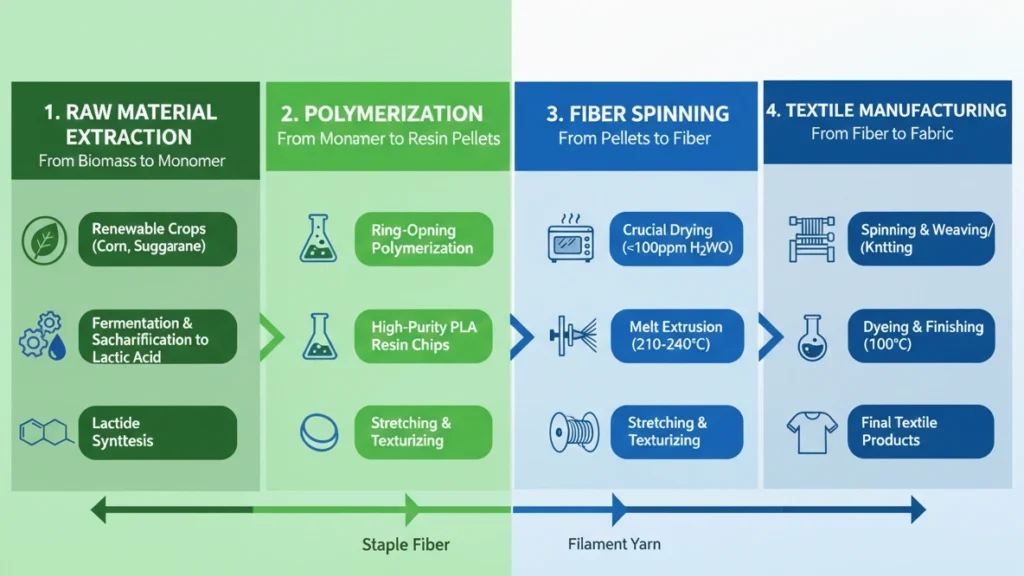
Scalable Fiber Configurations
The thermoplastic versatility of PLA allows it to be processed into various formats, meeting the rigorous demands of the global textile supply chain:
- Staple Fiber: Precision-engineered for high-speed carding and spinning with natural fibers, or for high-density nonwoven structures.
- Filament Yarn: Optimized for both multifilament and monofilament configurations, ensuring high tenacity and minimal breakage during weaving and knitting.
- Nonwoven Media: Direct conversion via spunbond, meltblown, or needle-punching technologies, providing a sustainable alternative for medical, hygiene, and industrial filtration.
Strategic Blending for Enhanced Functionality
PLA fiber excels in synergistic blends, allowing manufacturers to create differentiated materials that combine bio-based benefits with advanced performance characteristics.
| Blend Partner | Strategic Ratio | Technical Synergy | Primary Applications |
| Cotton | 30-50% PLA | Rapid moisture transport; superior wrinkle recovery | Sustainable activewear, premium bedding |
| Lyocell/Modal | 40-60% PLA | Enhanced structural integrity; optimized drape | Luxury eco-apparel, intimate wear |
| Wool | 20-40% PLA | Improved pill resistance; simplified garment care | Outerwear, tailored knitwear |
Overcoming Industrial Hurdles: Our Technical Partnership
Transitioning to bio-based polymers requires more than just raw materials; it requires precise process recalibration.We help our partners overcome the three primary challenges of PLA spinning:
- Strict Moisture Management: PLA is sensitive to hydrolysis at high temperatures. We provide protocols to ensure resin moisture is below 50–100 ppm via desiccant drying (typically 4-6 hours at 80°C) before extrusion to prevent molecular weight degradation.
- Controlled Thermal Profile: PLA has lower thermal stability than PET. We recommend a declining temperature profile in the extruder, with melt temperatures ideally kept between 220°C and 240°C to maintain high tenacity and prevent yellowing.
- Dyeing & Finishing Excellence: PLA reaches saturation with disperse dyes at 100°C – 110°C. Exceeding 115°C may lead to fiber shrinkage or loss of strength. Our team provides specific “dyeing curves” to maximize color fastness while preserving fiber integrity.
Refining your processing parameters for PLA?
Collaborate with our technical specialists to recalibrate your drying and extrusion protocols for consistent fiber quality.
Key Market Applications
The versatile molecular structure of PLA resin enables fiber production that meets the rigorous demands of diverse industrial sectors. By integrating our high-purity PLA grades, manufacturers can capture emerging market premiums while addressing the global shift toward circularity.
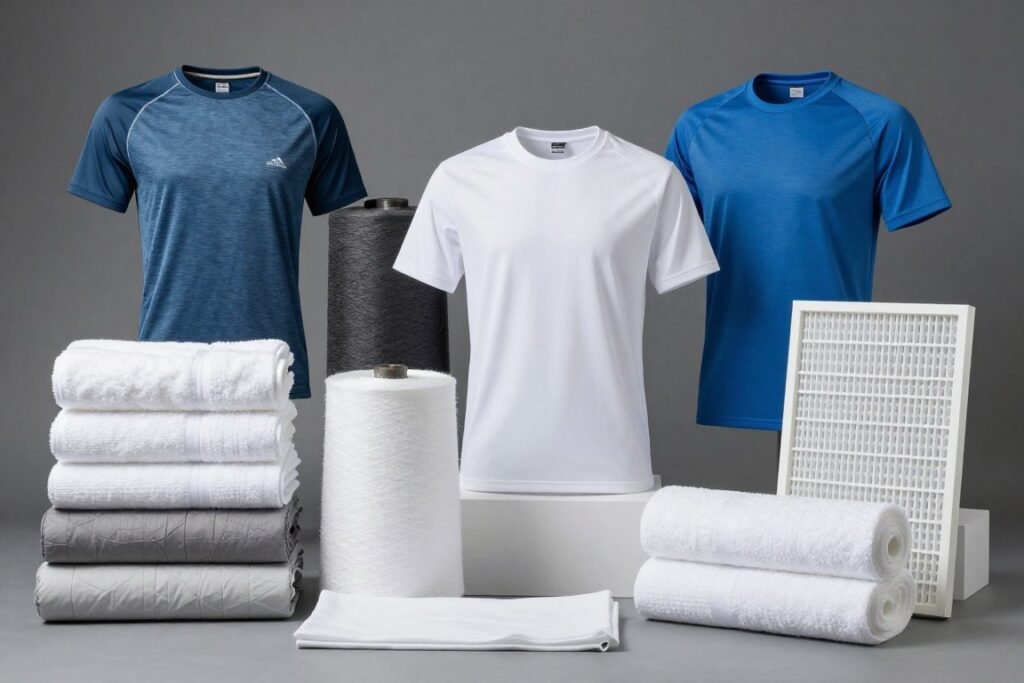

Performance Apparel and Intimate Wear
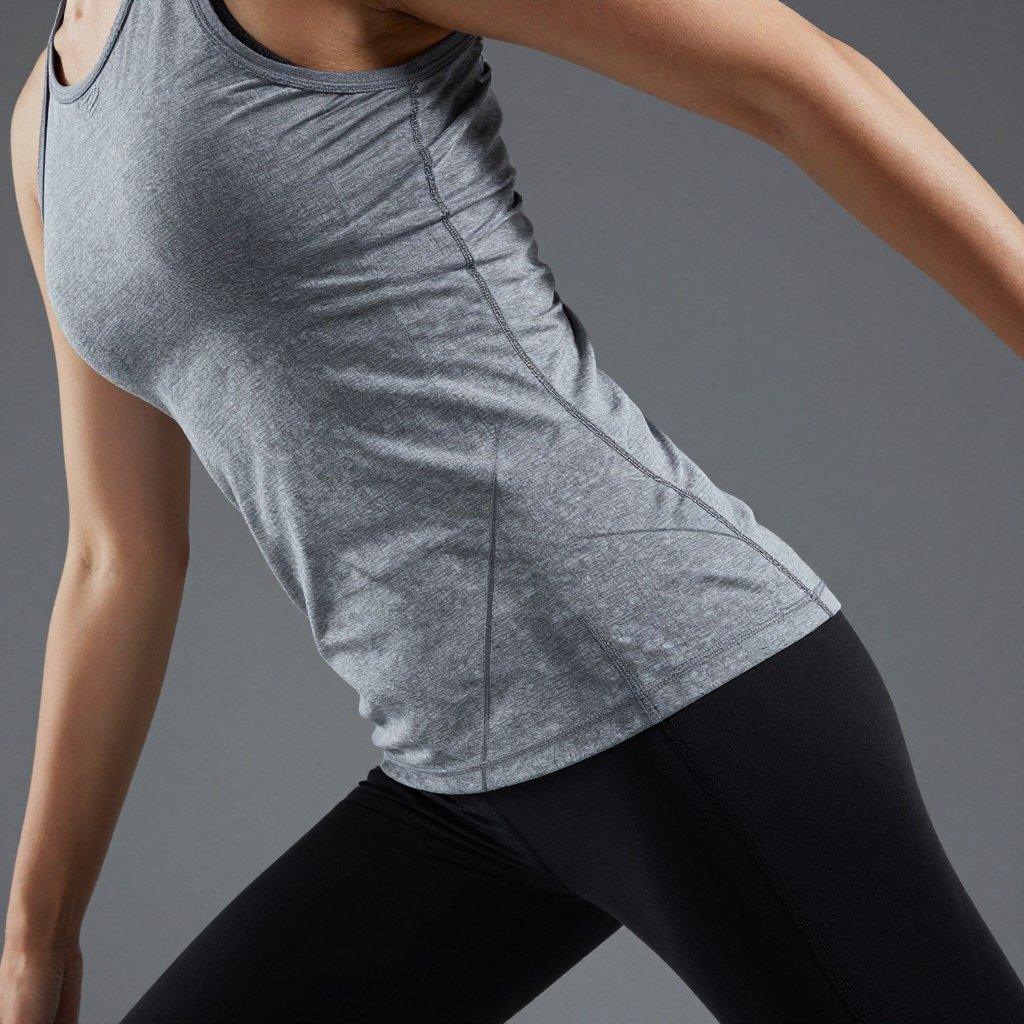

Biodegradable fiber creates a distinct competitive advantage in the Activewear and Base-layer segments. Its natural pH-neutrality and inherent bacteriostatic properties offer a “skin-friendly” marketing hook that synthetic alternatives lack. For high-performance apparel, PLA’s capillary action facilitates rapid moisture transport, ensuring comfort during high-intensity activity.Crucially, its low-carbon origin and skin-friendly functionalism allow apparel brands to meet ESG targets and command a premium, even without relying on changes in consumer disposal habits.
High-Growth Nonwovens and Hygiene
In the wake of tightening Single-Use Plastics (SUP) regulations, PLA resin has become the benchmark for sustainable nonwovens. For short-life applications where recovery is difficult, such as hygiene and agricultural textiles, biodegradable fiber offers a practical circular pathway, allowing brands to meet ESG targets without relying on changing consumer disposal habits.
- Hygiene Products: Biodegradable diaper liners and feminine care items that align with eco-conscious consumer expectations.
- Medical Textiles: Biocompatible wound dressings and surgical disposables that simplify medical waste management through bio-assimilation.
- Filtration Media: High-efficiency air and liquid filters that offer a lower carbon footprint and simplified end-of-life disposal.
Technical and Agricultural Solutions

The functional longevity of PLA is uniquely suited for Geotextiles and Agricultural applications. In erosion control and seedling protection, PLA provides the necessary structural integrity for the duration of the project before safely returning to the soil. This eliminates the labor-intensive recovery costs associated with traditional petroleum-based polymers. Furthermore, in Automotive Interiors (in specific blends or bio-composites), PLA-based upholstery and headliners contribute significantly to vehicle lightweighting goals and “Green Cabin” certifications.
Collaborative Material Development
Beyond standardized applications, our team supports the development of customized fiber specifications—from high-tenacity industrial yarns to ultra-soft microfiber blends. By aligning resin viscosity and additives with your specific application, we help you transform sustainable potential into market-leading textile products.
PLA (Polylactic Acid) Performance Rating
Why Partner With Us?
Success in the bio-based textile market requires a partner who bridges the gap between resin science and industrial-scale production.
- Premium Inventory: We maintain a strategic stock of Ingeo™ 6-Series (the global benchmark for fiber grades) and specialized high-heat resins.
- Traceability & Compliance: We provide full documentation, including GRS (Global Recycled Standard), BPI/DIN CERTCO compostability certifications, and OEKO-TEX Standard 100 compliance.
- Trial Risk Mitigation: Our engineers assist in your first melt-spinning trials to ensure parameter synchronization, reducing waste and downtime.

Specialized Portfolio for Fiber Excellence
We maintain a strategic inventory of Ingeo™ 6-Series, specifically engineered for high-performance fiber spinning. Our team provides precise guidance on selecting the optimal grade to match your mechanical and thermal requirements:
Ingeo™ 6201D
The industry standard for apparel filaments and staple fibers, optimized for high crystallization rates and superior tensile strength.
Ingeo™ 6202D
A versatile grade with a lower melting point, ideal for producing the sheath in sheath-core bicomponent fibers or as a specialized binder fiber.
Ingeo™ 6100D & 6060D
Robust solutions for heavy-denier industrial yarns, BCF carpet fibers, and high-flow nonwoven applications.

Refining your fiber specifications for the next collection?
Access our technical data sheets for Ingeo™ 6-Series and consult with our specialists to synchronize your melt-spinning parameters for peak performance.
Request Samples
Evaluate our Ingeo fiber quality firsthand with complimentary material samples.
Conclusion: The Future of Textiles is Bio-Circular
The shift toward circularity has evolved from a voluntary sustainability initiative into a mandatory entry ticket for the global textile market. As regulatory frameworks and carbon transparency standards become increasingly stringent, integrating high-purity PLA resin is no longer an experimental option but a strategic necessity. Early adoption of these advanced biopolymers allows forward-thinking manufacturers to occupy the strategic heights of material innovation, effectively future-proofing their supply chains against the inevitable rise in fossil-based polymer levies.
The unique synergy of industrial processability, skin-friendly functionalism, and carbon-negative potential positions PLA as the definitive successor to traditional synthetics. Our role is to ensure this material transition is both technically viable and commercially rewarding. By incorporating specialized Ingeo™ 6-Series resins into your portfolio, you secure a resilient, high-performance feedstock that aligns with the premium demands of a bio-conscious global consumer base.
We invite you to take the next step in this industrial transformation. Contact our technical specialists to obtain high-grade PLA resin samples, optimized melt-spinning trial parameters, and comprehensive carbon-reduction data. Together, we can redefine the fabric of the future—ensuring your products are not only manufactured for today’s market but engineered for a circular tomorrow.
Align your supply chain with tomorrow’s environmental mandates.
Let’s discuss how to integrate high-purity PLA resins into your portfolio to achieve verifiable carbon reductions and market differentiation.
Frequently Asked Questions About PLA Fiber
How does PLA fiber compare to conventional polyester in terms of durability?
In standard textile applications, PLA fiber provides mechanical performance equivalent to petroleum-based polymers. While its tensile strength ranges from 4.5–5.5 cN/dtex (comparable to PET’s 5.0–7.0 cN/dtex), PLA excels in UV stability, resisting yellowing and fiber degradation far longer than polyester when exposed to sunlight. Furthermore, PLA’s high modulus provides excellent resilience and dimensional stability, ensuring that fabrics maintain their shape and “new” feel through repeated wear and laundering cycles.
What processing adjustments are needed when switching from polyester to PLA fiber?
Our fiber-grade PLA resins are designed for seamless integration into existing melt-spinning lines with minimal retooling. The primary adjustment involves optimizing the thermal profile; since PLA has a melting point of 165–175℃, processing temperatures are typically 40–60℃ lower than for polyester, leading to significant energy savings. Crucially, we recommend a rigorous pre-crystallization and drying protocol (achieving moisture levels below 50 ppm) to prevent hydrolytic degradation during extrusion. Our technical specialists provide on-site guidance for adjusting throughput speeds and cooling quench air to ensure optimal filament formation.
Under what conditions will PLA fiber biodegrade?
PLA fiber is engineered for industrial circularity. It undergoes complete mineralization—returning to CO₂ and water—within 60 days under industrial composting conditions (regulated at approximately 58℃ with high humidity and microbial activity) as per EN 13432 or ASTM D6400 standards. While it remains stable and durable in ambient warehouse or retail environments, its bio-based origin ensures it does not contribute to persistent microplastic pollution. This provides a definitive end-of-life solution for technical textiles and single-use hygiene products that are otherwise difficult to recycle.
Is PLA fiber more expensive than conventional polyester?
While the initial resin cost carries a premium, the total value proposition often favors PLA in a decarbonizing market. The price gap is rapidly narrowing due to localized capacity expansions and optimized feedstock technologies. Moreover, manufacturers often realize operational savings through lower dyeing temperatures (90–110℃) and reduced energy consumption during extrusion. When factoring in the ability to command “Green Premiums” from eco-conscious brands and the strategic hedging against future carbon border taxes (CBAM), PLA becomes a highly competitive asset for forward-thinking supply chains.


