Polybutylene Terephthalate reinforced with 30% glass fiber (PBT-GF30) represents a critical engineering thermoplastic engineered for environments demanding high structural integrity and thermal endurance. Integrating a precise volume of glass fiber into the semi-crystalline PBT matrix enables a significant leap in tensile strength and flexural modulus compared to unfilled grades. This material excels in maintaining dimensional stability and dielectric integrity under fluctuating humidity—a distinct advantage over moisture-sensitive polyamides. Whether addressing the heat aging requirements of automotive under-the-hood components or the intricate tolerances of precision electronic connectors, PBT GF30 provides a reliable balance of creep resistance and chemical inertness.
What is PBT-GF30?
PBT-GF30 is a high-performance engineering composite comprising Polybutylene Terephthalate reinforced with a standardized 30% glass fiber loading by weight. This specific fiber concentration transforms the base semi-crystalline polyester into a rigid structural material, elevating its heat deflection temperature and tensile modulus significantly. At the molecular level, the characteristic butylene backbone facilitates rapid crystallization during injection molding—a critical factor for optimizing cycle times in high-volume production.
Furthermore, the reinforcement matrix mitigates inherent polymer shrinkage, ensuring precise dimensional tolerances even in complex geometries. While the GF30 variant ensures stability under mechanical stress, the performance originates from the high-quality base polyester. To understand the fundamental characteristics of the unfilled resin, refer to our comprehensive analysis: The Benchmark of PBT: A Technical Overview of Duranex 2002.

Microscopic view showing glass fiber distribution in PBT-GF30
Key Properties and Features of PBT-GF30
Mechanical Properties
The 30% glass fiber reinforcement provides PBT with high tensile strength (145–230 MPa) and a tensile modulus of approximately 10,000 MPa. These attributes enable components to withstand significant structural loads while maintaining tight tolerances.
Thermal Properties
With a melting point of approximately 225°C and a heat deflection temperature (HDT) of 205°C at 1.8 MPa, PBT GF30 maintains mechanical integrity across a wide range. It supports continuous operating temperatures up to 110°C.
Electrical Properties
Volume resistivity exceeding 10¹⁴ Ω cm and a Comparative Tracking Index (CTI) of 350V make it a reliable choice for electrical housings. Low moisture absorption ensures these characteristics remain stable in humid environments.
Chemical Resistance
The material offers broad resistance to hydrocarbons and automotive fluids. While durable in most industrial settings, it has limited resistance to strong acids and hydrolysis in water above 60°C.

Laboratory testing of PBT GF30’s mechanical properties
| Property | Value | Unit | Test Method |
| Density | 1.46–1.53 | g/cm³ | ISO 1183 |
| Tensile Modulus | 9,000–10,500 | MPa | ISO 527-2 |
| Tensile Strength | 145–230 | MPa | ISO 527-2 |
| Elongation at Break | 3–6 | % | ISO 527-2 |
| Charpy Impact Strength | 37–65 | kJ/m² | ISO 179-1/1eU |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 205 | °C | ISO 75 (1.8 MPa) |
| Water Absorption (24h) | 0.02–0.2 | % | ISO 62 |
Featured PBT-GF30 Grades and Technical Selection
Selecting the appropriate grade requires aligning application demands with specific material formulations. Our portfolio includes market-leading solutions optimized for diverse engineering challenges:
Premium Precision Grades (Polyplastics)
- Duranex® 3300 (General Purpose): The industry benchmark for PBT GF30, offering an optimized balance of mechanical strength and melt flow. For a deeper technical dive, explore our Comprehensive Guide to Duranex 3300 PBT Properties and Processing.
- Duranex® 733LD (Low Warpage): Engineered with specialized technology to minimize anisotropic shrinkage, ensuring exceptional dimensional stability and flatness in large-format or precision components.
- Duranex® 3316 (Flame Retardant): Specifically formulated for electrical safety, achieving UL94 V-0 compliance; ideal for high-reliability connector housings and switchgear.
High-Efficiency Supply Grades (CCP)
- CCP PBT-3030 (Standard Grade): Engineered for consistent processing stability and mechanical reliability; the preferred choice for high-volume automotive and industrial housings.
- CCP PBT-4130 / 4830 (Flame Retardant): High-performance FR grades offering stable electrical properties and safety compliance for power distribution components.
- CCP PBT-1100 series (High Flow): Optimized for complex, thin-walled geometries, ensuring high-speed production without compromising structural integrity.
Specialized Global Standards
- BASF Ultradur® B 4300 G6: A premium grade featuring high toughness and superior flowability, frequently specified for automotive motor housings and wiper systems.
- Celanese Celanex® 3300: A high-flow, general-purpose grade designed for the efficient processing of intricate, thin-walled geometries in global automotive architectures.

Visual comparison of Duranex® 733LD with Duranex® 3316 materials
Manufacturing Process and Variants
Injection molding represents the primary manufacturing pathway for PBT GF30, as the material’s excellent rheological behavior facilitates the production of complex, thin-walled geometries. The mechanical integrity of the final component is heavily contingent upon the glass fiber orientation established during the melt phase. This inherent anisotropy requires strategic tool design and precise gate positioning to mitigate differential shrinkage and potential warpage. Critical processing parameters, including melt temperature (typically 240°C–260°C) and controlled injection velocities, must be calibrated to ensure optimal fiber distribution and minimize internal residual stresses.

Injection molding process for PBT-GF30 components
The technical versatility of PBT-GF30 is further extended through specialized formulations tailored to specific environmental stressors:
Flame-Retardant (FR) Grades
Integrated with halogenated or halogen-free systems to achieve UL94 V-0 ratings, these variants are essential for high-voltage connectors and circuit breakers where ignition prevention is a non-negotiable safety requirement.
Hydrolysis-Stabilized Grades
While standard PBT is susceptible to polymer chain scission in aqueous environments, these stabilized grades maintain their molecular weight and mechanical properties when exposed to hot water or high-humidity conditions (above 60°C).
Low-Warpage Variants
Specialized grades, such as those incorporating mineral fillers or specific nucleation agents, are engineered to balance the anisotropic effects of glass fibers, ensuring high dimensional flatness in large-format structural components.
Thermo-Oxidative Stabilized Grades
Formulated with advanced antioxidant packages, these resins resist long-term thermal degradation, making them the industry standard for continuous-use automotive under-the-hood applications.
Applications Across Industries
The technical synergy of mechanical rigidity and chemical resilience enables PBT-GF30 to serve as a high-performance alternative to metal alloys. Its low creep and high dimensional precision make it indispensable in sectors where failure-free operation is mandatory.
Automotive Engineering
Leveraging thermal endurance (HDT 205°C) and resistance to corrosive automotive fluids:
- Electrical Architecture: High-pin-count PBT-GF30 connectors, fuse boxes, and relay housings.
- Under-hood Components: PBT-GF30 sensor housings, throttle bodies, and ignition system parts (often utilizing high-flow grades like Celanex 3300).
- Exterior Systems: Windshield wiper arms and mirror bracket reinforcements.
- Powertrain: Water pump impellers and thermostat housings requiring hydrolytic stability.
Electrical & Electronics
Utilizing superior dielectric strength and flame-retardant compliance:
- Safety Equipment: Circuit breaker components and switchgear housings requiring UL94 V-0 ratings (e.g., PBT4130).
- Connectivity: High-voltage terminal blocks and heavy-duty connector systems.
- Precision Windings: Dimensional stability for coil bobbins and transformer housings.
- Thermal Management: LED lighting heat-sink frames and cooling fan blades.
Industrial Engineering
Exploiting low friction coefficients and high fatigue resistance:
- Fluid Technology: Corrosion-resistant pump housings, impellers, and valve bodies.
- Kinematic Components: Precision gears, cogs, and cams that maintain tolerances under load (standard grades like PBT3030 are frequently specified).
- Hardware: Heavy-duty tool handles, brackets, and structural mounting plates.
- Bearing Systems: Wear-resistant bearing retainers and sliding elements.

Diverse applications of PBT GF30 across automotive, electrical, and industrial sectors
Explore PBT GF30 for Your Application
Our technical team can help evaluate if PBT GF30 is the right material for your specific requirements. Request a consultation to discuss your project needs.
Challenges, Limitations, and Solutions
Balanced engineering requires a thorough understanding of the operational constraints inherent to PBT-GF30. While the material offers superior rigidity and dielectric strength, specific environmental and geometric factors necessitate strategic material selection and design adjustments.
Advantages
- High tensile strength (145–230 MPa) and exceptional flexural modulus.
- Superior creep resistance and low thermal expansion across operating temperatures.
- High dielectric strength and volume resistivity (> 10¹⁴ Ω・ cm).
- Extremely low water absorption (0.02–0.2%), ensuring consistent properties in humid environments.
- Broad resistance to automotive fluids, hydrocarbons, and weak acids/bases.
- Excellent melt flow and rapid crystallization for shortened cycle times.
Limitations
- Degradation risk in hot water or steam environments exceeding 60°C.
- Vulnerability to stress concentration at sharp corners or thin-to-thick transitions.
- Differential shrinkage and strength variations due to glass fiber orientation.
- Potential for surface chalking and mechanical loss upon prolonged outdoor exposure.
- Abrasive fiber content affecting the wear of mating plastic-to-plastic surfaces.
Design Considerations and Solutions
Design considerations for PBT GF30 components: proper vs. improper design examples
Addressing Hydrolysis Concerns
Standard PBT-GF30 is susceptible to polymer chain scission when exposed to hot water (above 60°C) or high-pressure steam.For automotive cooling systems or appliance components, utilizing hydrolysis-stabilized grades significantly extends service life by neutralizing moisture-induced degradation.
Anisotropy and Warpage
Fiber orientation during the injection phase causes differential shrinkage. Optimizing gate locations and utilizing Moldflow analysis are essential to align fibers with the primary stress direction and minimize distortion in large, flat components.
Notch Sensitivity and Brittleness
The high glass fiber loading increases stiffness but makes the material sensitive to sharp corners and stress concentrators.Designers should implement generous radii (minimum 0.5–1.0 mm) and maintain uniform wall thickness. High-toughness grades, such as specialized variants of Duranex 3300, can be specified for high-impact assemblies.
Environmental Degradation
Untreated PBT-GF30 exhibits UV sensitivity, leading to surface chalking and mechanical loss over time. For outdoor infrastructure, the addition of carbon black or specialized UV stabilizers (found in grades like PBT4830) provides necessary weatherability.
Future Trends and Sustainability
Technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks are redefining the lifecycle and performance benchmarks of PBT-GF30. As global industrial sectors prioritize decarbonization and circular economy principles, the evolution of this composite focuses on balancing engineering excellence with environmental stewardship.
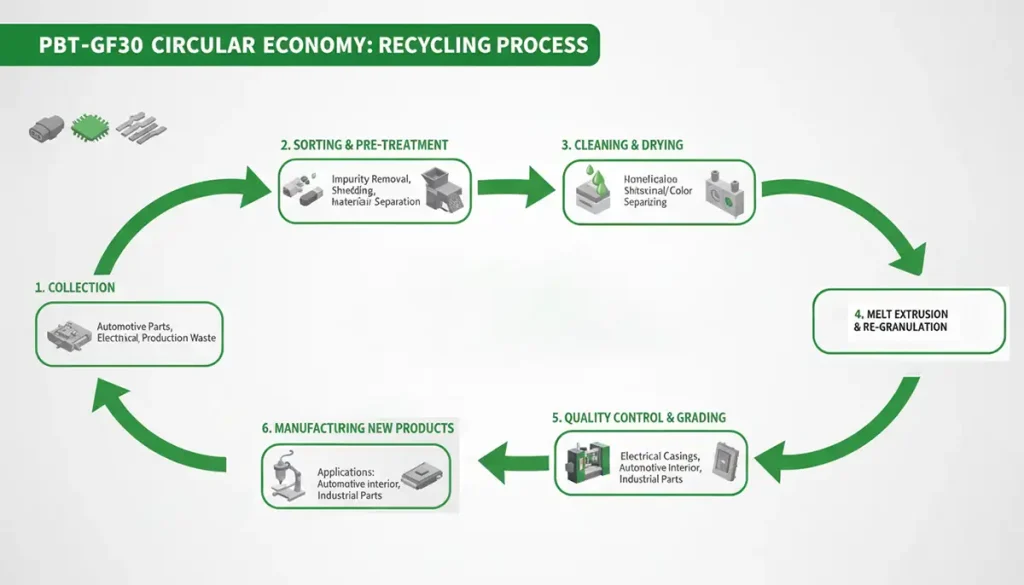
Sustainable manufacturing and recycling processes for PBT GF30
Advanced Material Recovery
Mechanical recycling remains a primary focus, though maintaining structural integrity requires managing fiber length degradation during reprocessing. Emerging chemical recycling techniques—specifically depolymerization—offer a sophisticated alternative, breaking down the polymer into its constituent monomers to produce “virgin-quality” resin. Leading manufacturers are increasingly introducing Post-Consumer Recycled (PCR) or Post-Industrial Recycled (PIR) grades that meet the rigorous durability standards of traditional automotive and electronic components.
Bio-Based Resin Development
Strategic shifts toward renewable feedstocks have led to the commercialization of partially bio-based PBT. By incorporating bio-sourced 1,4-butanediol (BDO) derived from sustainable biomass, these formulations significantly reduce the carbon footprint without compromising the material’s characteristic melting point, chemical resistance, or dielectric strength.
Functional Hybridization and E-Mobility
Future-ready PBT-GF30 is evolving through the integration of multifunctional additives to meet the demands of Electric Vehicle (EV) architectures. This includes the development of laser-transparent grades for sensor housings and high-voltage signal orange variants (frequently derived from base models like PBT-4830) that maintain color stability and electrical insulation under long-term thermal aging.
Conclusion
The technical synergy of mechanical rigidity, dielectric stability, and thermal endurance positions PBT GF30 as a cornerstone material for precision engineering. Its ability to maintain critical tolerances under sustained mechanical loads and harsh chemical exposure ensures long-term reliability in automotive, electronic, and industrial hardware assemblies.
Successful implementation of PBT-GF30 relies on a nuanced alignment between application requirements and specific grade characteristics. Whether utilizing a high-flow general-purpose grade like Celanex 3300 for complex geometries or a robust standard grade such as PBT3030 for structural brackets, engineers must account for factors like fiber-induced anisotropy and hydrolytic limits during the design phase. As the industry pivots toward electrified powertrains and circular economy frameworks, the emergence of high-voltage safe and recycled-content variants will further expand the utility of this glass-reinforced composite.
By integrating these material insights with optimized processing techniques, manufacturers can achieve superior component performance while meeting evolving sustainability mandates. Navigating the diverse landscape of available PBT-GF30 formulations requires professional technical expertise to ensure the optimal balance of cost-efficiency and functional excellence.
Ready to Evaluate PBT GF30 for Your Project?
Our technical team provides comprehensive support for the Polyplastics, CCP, BASF, and Celanese portfolios. We can assist with material data sheets, grade comparisons, and stock availability to ensure your production remains efficient.
About Our PBT-GF30 Compounds
Expertise in thermoplastic engineering underpins our supply chain, ensuring every batch of PBT-GF30 complies with stringent industrial requirements. We bridge the gap between global resin synthesis and localized manufacturing needs by distributing industry-leading PBT GF30 from Polyplastics, Celanese, and CCP. This strategic positioning provides our clients with a dual advantage: guaranteed material authenticity and localized technical troubleshooting. Our portfolio encompasses a diverse range of 30% glass fiber reinforced compounds—from high-stiffness structural grades like the Duranex® and Celanex® series to specialized UL94 V-0 flame-retardant and hydrolysis-stabilized formulations.

Our state-of-the-art facility producing premium PBT-GF30 compounds
Navigating the complexities of high-performance thermoplastics requires more than a supplier; it demands a technical partner. Whether you are addressing warpage in a large-format housing or seeking a cost-effective alternative to die-cast metal, our material engineers are available to provide comparative data analysis and processing optimizations tailored to your specific mold requirements. Technical support extends throughout the product development lifecycle, offering data-driven guidance on material selection and mold-flow analysis to mitigate common challenges like anisotropic shrinkage. By leveraging a robust logistics infrastructure, we ensure a reliable supply of high-performance PBT-GF30, enabling manufacturers to optimize production efficiency and maintain the functional integrity of their components.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does PBT GF30 mean?
PBT GF30 designates Polybutylene Terephthalate reinforced with 30% glass fiber by weight. This specific loading is an industry standard designed to optimize the synergy between the polymer matrix and reinforcement. While base PBT offers excellent electrical properties and chemical resistance, the 30% glass fiber content significantly elevates tensile strength and reduces mold shrinkage, ensuring high-precision dimensions for structural engineering components.
What are the advantages of PBT-GF30?
The primary advantage lies in its exceptional dimensional stability and high heat deflection temperature (HDT of 205°C at 1.8 MPa). PBT GF30 maintains robust dielectric strength even in high-humidity environments due to its extremely low water absorption (typically 0.02-0.2%). Grades like PBT3030 provide a reliable balance of stiffness and chemical resilience against automotive fluids, making it a superior alternative to die-cast metals in weight-sensitive applications.
How strong is PBT GF30?
The material exhibits a high tensile modulus of approximately 10,000 MPa and tensile strength ranging from 145 to 230 MPa. These values, alongside a flexural strength of up to 230 MPa, vary based on the specific resin viscosity and glass fiber quality utilized in formulations like the Celanex or Duranex series. Its impact resistance (37–65 kJ/m²) ensures durability under mechanical stress, though final strength is also influenced by fiber orientation during the injection molding process.
Can PBT-GF30 be recycled?
PBT GF30 is technically recyclable through mechanical grinding, though repeated thermal processing causes glass fiber breakage, which may lead to a gradual reduction in mechanical properties. Advanced chemical recycling is currently expanding to recover the base polymer without degradation. To meet sustainability targets, many manufacturers now supply grades incorporating Post-Consumer Recycled (PCR) or Post-Industrial Recycled (PIR) content, maintaining rigorous performance standards while reducing the overall carbon footprint.


