Polylactic Acid (PLA) anchors this sector, offering an optimal balance of superior extrudability, minimal warping, and bio-based sustainability. From an industrial manufacturing perspective, these filament-level advantages are fundamentally determined upstream—by the consistency, purity, and molecular stability of the PLA 3D filament raw material used during filament extrusion.
Market data from 2026 indicates that “Batch-to-Batch Consistency” has become the decisive factor for industrial scaling, as the refined polymerization of PLA offers a more stable production window compared to the volatile thermal properties of ABS. For filament manufacturers operating multi-line extrusion systems, stable PLA plastic filament pellets quality directly translates into tighter diameter control, reduced filter changes, and higher extrusion uptime.
This guide dissects the comparative cost structures of these polymer matrices, analyzing how raw material density, processing throughput, and thermal requirements influence your manufacturing margins and final product viability.
Current PLA Consumables Price Details
Market stabilization in 2026 follows significant supply chain recalibrations, with standard PLA now positioned between $15 and $22 per kilogram. This pricing stability is largely supported by the maturation of the global PLA plastic filament raw material supply chain, where large-scale polymerization capacity and standardized pellet specifications have reduced upstream cost volatility.
However, a comprehensive fiscal analysis must extend beyond the invoice price per kilogram to account for the “Yield-Adjusted Cost”—where PLA’s low failure rate frequently results in the lowest cost per finished part.In practice, filament producers using high-consistency PLA pellets often report lower scrap ratios and faster line stabilization during color or batch changeovers.
Factors Influencing PLA Pricing
Technical Specifications: Precision manufacturing remains a primary price driver. High-grade resins maintaining a diameter tolerance of ±0.02mm command a $3–$5 premium.At the filament production level, achieving this tolerance is highly dependent on PLA resin melt flow stability (MFR consistency) and moisture control prior to extrusion.The reduction in extrusion-related downtime typically yields a net operational saving of 12–18% in high-speed environments.
Functional Aesthetics: Specialized finishes reflect the complexity of additive compounding.These specialty filaments require PLA base resins with high thermal clarity and additive compatibility to ensure uniform dispersion during twin-screw compounding.
- Silk PLA: $22-28 per kg
- Matte PLA: $20-25 per kg
- Metallic PLA: $24-30 per kg
- Glow in the dark PLA: $25-32 per kg
Volumetric Scaling: Bulk procurement offers substantial operational savings for large-scale plastic processing. Similarly, bulk sourcing of filament-grade PLA pellets enables manufacturers to maintain batch continuity across extended production cycles, reducing color drift and mechanical variation.
Sustainability and Certification:As environmental compliance becomes a global manufacturing standard, PLA’s low carbon footprint provides a strategic advantage.More filament manufacturers now prioritize PLA resins with traceable bio-based content and internationally recognized certifications to meet both regulatory requirements and end-customer demands.
PLA vs. ABS vs. PETG: Cost & Performance Comparison
Material selection frameworks in the 2026 additive manufacturing landscape prioritize the equilibrium between polymer-specific performance and total operational expenditure. The following technical benchmarks provide a comparative overview of the three most prevalent thermoplastics utilized in industrial and commercial production.
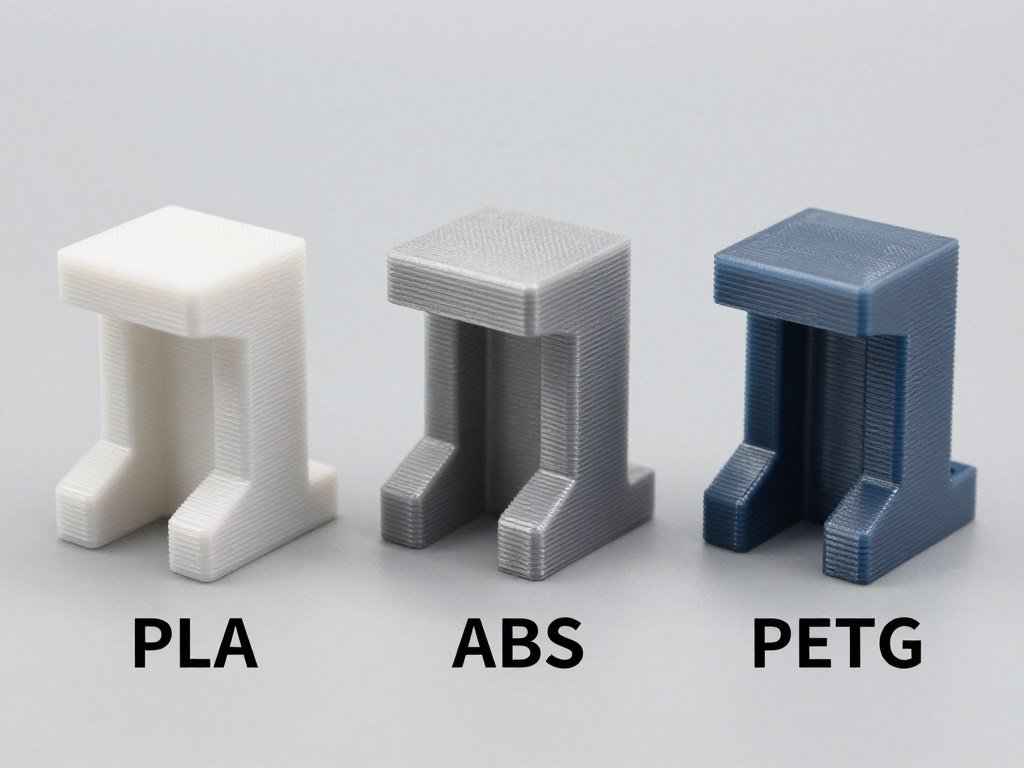
Test prints showing surface finish and detail capabilities of PLA, ABS, and PETG filaments
| Feature | PLA | ABS | PETG |
| Cost per kg (2026) | $15–22 | $16–25 | $18–28 |
| Density (kg/m³) | 1,240 | 1,045 | 1,270 |
| Glass Transition Temp | 60–65°C | 105°C | 80–85°C |
| Operational Throughput | High (High Yield) | Low (Warpage Risk) | Medium |
| Mechanical Integrity | High Rigidity | High Impact Resistance | High Toughness |
While ABS and PETG offer specific performance advantages, their filament processing windows are narrower and more sensitive to thermal fluctuation, increasing dependence on controlled environments and operator experience.
Material Properties Deep Dive
PLA : The Efficiency Benchmark
Optimized for high-speed extrusion, PLA offers the widest processing window. Its predictable crystallization minimizes diameter drift, allowing for maximum line uptime and the lowest energy consumption per ton of filament.
Industrial Edge
- Near-zero warping;
- carbon-neutral compliance; superior melt stability.
ABS : Thermal & Impact Resilience
While offering high heat resistance, ABS presents manufacturing challenges due to its high thermal contraction. It requires precisely controlled chamber temperatures and robust VOC filtration, increasing operational overhead.
Industrial Edge
- High ductility;
- low density (1,045 kg/m³) for higher part yield per kg.
PETG: The Mechanical Middle Ground
PETG offers a balance of toughness and chemical resistance but demands rigorous moisture management. For filament producers, PETG requires high-performance desiccant drying to prevent hydrolytic degradation during extrusion.
Industrial Edge
- Superior layer adhesion;
- food-contact safety;
- high impact strength.
These materials typically require tighter process control and higher energy input at both the resin drying and filament extrusion stages.
Cost Per Print Analysis
A comprehensive cost assessment must factor in density-driven material consumption and the financial impact of production failures. The table below illustrates the projected costs for a standard 100g industrial component.
| Cost Factor | PLA | ABS | PETG |
| Material Cost (100g) | $1.50–2.20 | $1.60–2.50 | $1.80–2.80 |
| Energy Consumption | Low | High | Medium |
| Yield Rate Risk (Failures) | Low (5–10%) | High (15–30%) | Medium (10–20%) |
| Total Estimated TCO | $1.65–2.45 | $2.00–3.25 | $2.10–3.35 |
Lower failure rates in PLA printing are closely linked to filament uniformity, which itself depends on the quality of PLA plastic filament pellets and moisture stability during pellet processing.
Commodity PLA vs Filament-Grade PLA Pellets
The Bridge: While the chemical formula of PLA remains identical, the thermomechanical profile of the resin dictates the operational efficiency of your extrusion line. For high-volume producers, the price gap between generic resin and specialized pellets is often recovered within the first few hours of production through minimized downtime.
Why Raw Material Quality Determines Filament Profitability
PLA is often discussed as a single material, but not all PLA resins are engineered for filament extrusion.In industrial production, filament profitability depends less on resin price and more on pellet-level consistency and extrusion stability.
Commodity PLA: Designed for Injection Molding or General Processing, Not Filament Lines
- Wide MFR variation, causing unstable melt pressure
- Inconsistent moisture content, increasing bubbling and surface defects
- Unpredictable crystallization, leading to diameter drift
- Longer stabilization times during batch or color changeovers
These issues may be manageable in small-scale setups but significantly impact multi-line, high-speed filament production.
Filament-Grade PLA Pellets: Engineered for Extrusion Stability
- Tightly controlled MFR and molecular weight distribution
- Low, consistent moisture levels
- Predictable cooling behavior for ±0.02mm diameter control
- Reliable batch-to-batch consistency for continuous runs
From a cost perspective, evaluating PLA solely by price per kilogram is misleading.
Filament-grade PLA typically reduces scrap, downtime, and energy waste—resulting in a lower cost per usable meter, even when the pellet price is slightly higher.
For manufacturers targeting scalable production, tight tolerances, and predictable output, PLA pellet quality is not a material detail—it is a production strategy.For a detailed technical comparison of commodity vs filament-grade PLA pellets, see our in-depth guide → Commodity PLA vs Filament-Grade PLA
Not All PLA Pellets Perform the Same in Filament Production
Commodity-grade PLA may meet basic specs, but filament-grade PLA pellets are engineered for stable extrusion, faster line speed, and lower scrap rates.
Best Applications for Each Filament Type
Effective material alignment transcends base procurement costs, requiring a precise match between polymer properties and operational environments. The following categorizations outline where each resin offers the highest industrial utility:

Ideal applications for each filament type: decorative (PLA), functional (ABS), and versatile (PETG)
PLA Best Uses
- Decorative items and figurines
- Architectural models
- Prototypes and concept models
- Low-stress indoor applications
- Educational projects
- Detailed models requiring minimal warping
Cost-Efficiency Rating: ★★★★★
PLA remains the preferred choice for decorative and non-functional prints due to its ease of printing and cost-effectiveness. For filament manufacturers, PLA is the most scalable material for high-volume production due to its forgiving processing window and stable resin behavior.
ABS Best Uses
- Functional mechanical parts
- Automotive components
- Outdoor applications
- Items exposed to heat (up to 105°C)
- Tools and fixtures
- Parts requiring post-processing (acetone smoothing)
Cost-Efficiency Rating: ★★★☆☆
Despite higher failure rates, ABS remains cost-effective for applications requiring its unique heat and impact resistance.
PETG Best Uses
- Food-safe containers
- Water-tight applications
- Mechanical parts with moderate stress
- Transparent or translucent items
- Medical applications
- Parts requiring chemical resistance
Cost-Efficiency Rating: ★★★★☆
PETG provides excellent value when you need a balance of strength, durability, and printability without ABS’s difficulties.
Temperature Resistance Comparison
Environmental temperature is a critical boundary condition. The following table illustrates how each material responds to common thermal stressors.

Heat resistance test showing deformation points of PLA, ABS, and PETG samples
| Temperature Scenario | PLA | ABS | PETG |
| Car Interior (Summer) | Likely to deform | Stable | Mostly Stable |
| Dishwasher | Likely to deform | Stable | May Deform |
| Hot Water (80°C) | Likely to deform | Stable | Stable |
| Refrigerator | Stable | Stable | Stable |
| Outdoor (Direct Sunlight) | Likely to deform | Stable | Mostly Stable |
Cost-Saving Tips for 3D Printing
Effective cost management in 3D printing extends beyond the initial procurement of PLA, ABS, or PETG. Implementing data-driven adjustments to production workflows and supply chain strategies can significantly enhance the ROI of additive manufacturing projects.

Practical cost-saving techniques for 3D printing: optimized infill, proper storage, and print settings
Parameter Optimization for Resource Efficiency
- Infill Calibration: Reducing infill to 10–15% for non-structural prototypes maintains aesthetic integrity while lowering material consumption and cooling time.
- Adaptive Layer Heights: Utilizing 0.2–0.3mm layers for functional iterations accelerates throughput; high-resolution 0.1mm settings should be reserved for final-stage validation.
- Batch Processing: Maximum build plate utilization reduces total pre-heating cycles, effectively lowering energy overhead per unit.
Quality Assurance and Risk Mitigation
- Preventative Maintenance: Monthly calibration of extrusion steps and kinematic lubrication mitigates mechanical failures that lead to high-cost scrap.
- Material Conditioning: Implementing active filament drying systems—particularly for PLA and PETG—ensures consistent flow and minimizes the risk of moisture-induced print failures.
- Iterative Testing: Small-scale geometry validation prevents large-format wastage during complex assembly production.
Strategic Procurement and Material Lifecycle
- Volumetric Purchasing: Migrating from standard 1kg units to 3kg or 5kg spools typically yields 15–25% cost reductions and improves batch-to-batch coloration consistency when sourcing high-quality PLA plastic filament raw material
- Direct-from-Supplier Partnerships: Establishing quarterly supply agreements with manufacturers or joining trade-level group buys secures wholesale pricing and stabilizes the supply chain against market volatility.
- Material Recovery: Utilizing filament joiners for remaining spool ends and tracking usage via digital scales ensures nearly 100% material utilization.
- Hybrid Manufacturing: Reinforcing hollow prints with low-cost internal hardware reduces the need for solid plastic infill in structural components.
At the production level, pre-dried PLA pellets with controlled moisture content significantly reduce filament bubbling, surface defects, and downstream print failures.
Why Choose Our Premium PLA Raw Material?
We supply PLA plastic filament raw materials that meet rigorous quality standards for molecular stability, purity, and moisture content control. Our PLA pellets are sourced directly from manufacturers with ISO and bio-based certifications, enabling filament producers to achieve:
Batch-to-Batch Consistency
Minimized diameter fluctuation ensures tighter filament tolerances (±0.02mm), reducing filter clogging and extrusion downtime.
High Melt Flow Rate Stability (MFR)
Supports faster line speeds and stable extrusion, increasing production throughput by up to 18%.
Controlled Moisture Levels
Pre-dried pellets reduce filament bubbling and surface defects, leading to higher print success rates and less waste. Moisture content is a critical factor in PLA extrusion and can significantly affect print quality. For a more in-depth understanding of how moisture impacts PLA properties, including drying techniques and performance optimization, read our full guide on How Moisture Affects PLA Performance.
Traceable Sustainability
Certified bio-based content supports environmental compliance and green manufacturing goals.
Conclusion

Various 3D printed objects showcasing the versatility of different filament types
PLA remains the operational benchmark for high-precision prototyping and rapid concept validation.For filament manufacturers, this performance consistency is rooted in the quality of the underlying PLA resin—where stable molecular weight distribution and controlled pellet specifications enable predictable extrusion and reliable end-use performance.
Successful procurement hinges on evaluating the total cost of ownership.Establishing direct partnerships with reliable PLA raw material suppliers allows filament producers to secure long-term batch consistency, technical support, and scalable supply as demand grows.
Ready to Scale PLA Filament Production — Without Increasing Failure Risk?
As filament production scales, raw material consistency becomes a process variable rather than a specification.
For manufacturers operating multi-line extrusion systems, pellet-level stability directly impacts diameter control, uptime, and yield.
If you are evaluating PLA raw materials for filament extrusion, we can help you:
- Assess batch-to-batch consistency under real extrusion conditions
- Compare yield-adjusted cost, not just price per kilogram
- Validate moisture stability and MFR consistency before full-scale adoption
Frequently Asked Questions
How much should PLA filament cost in 2026?
Standard industrial-grade PLA remains positioned between $15 and $22 per kilogram. This price bracket typically ensures a diameter tolerance of ±0.02mm and consistent batch-to-batch pigmentation. Premium resins or specialized additives—such as silk, matte, or carbon-fiber infusions—range from $22 to $32 per kilogram. While budget-tier materials exist below $15, they often introduce higher operational risks, including nozzle clogging and inconsistent mechanical integrity, which can increase the total cost of production.
Is PLA more expensive than other filaments?
PLA is the most cost-effective thermoplastic within the 2026 market, with base rates of $15–$22/kg compared to ABS ($16–$25/kg) and PETG ($18–$28/kg). Beyond the invoice price, PLA offers superior economic efficiency due to lower thermal processing requirements and a significantly higher success rate (yield). When factoring in electricity consumption and reduced hardware wear-and-tear, PLA provides the lowest total cost per finished part for most non-thermal applications.
How much does 1kg of PLA filament print?
A 1kg spool of PLA yields approximately 330–350 cubic centimeters of finished object volume, accounting for standard support structures and a 5% purge margin. In practical terms, this produces roughly 35–45 precision technical components or 15–20 medium-scale prototypes (approx. 15cm). Total yield is dictated by geometry optimization, with a 15–20% infill density serving as the industrial standard for balancing structural integrity with material conservation.
What are the key material properties of PLA filament?
PLA (Polylactic Acid) is defined by its superior surface fidelity and dimensional accuracy. Its core technical profile includes:
- Mechanical Performance: High tensile strength (50–70 MPa) and a high elastic modulus, providing a rigid, high-fidelity finish.
- Physical Properties: A density of 1,240 kg/m³ ensures a solid structural feel compared to lower-density alternatives like ABS.
- Thermal Thresholds: A glass transition temperature (Tg) of 60–65°C, optimized for low-energy extrusion and minimal thermal contraction.
- Sustainability: Certified industrial-grade compostability, derived from renewable bio-based feedstocks.2
- Operational Strengths: Exceptional ease of printing and excellent interlayer adhesion with negligible warpage.
- Material Constraints: Inherent brittleness compared to technical elastomers; limited UV stability and thermal resistance (softening occurs above 50°C).
These properties position PLA as the primary benchmark for indoor mechanical prototypes, high-detail aesthetic models, and precision-dependent concept validations.
What is the density of PLA filament in kg/m³?
Standard PLA resin has a density of approximately 1,240 kg/m³. This is roughly 18% higher than ABS (1,045 kg/m³) and marginally lower than PETG (1,270 kg/m³). For procurement and logistics planning, this means that while PLA offers superior printability, a finished PLA component will be heavier than an identical ABS part. Understanding this density variance is essential for calculating accurate volumetric shipping costs and per-unit material consumption.
What is the temperature resistance of different 3D printer filaments?
Thermal thresholds define the operational boundaries for each filament. PLA exhibits low heat resistance, with structural softening occurring above 50°C (Tg 60–65°C). ABS provides high-temperature stability, maintaining integrity up to 90°C (Tg 105°C), while PETG offers a moderate middle ground suitable for environments up to 75°C (Tg 80–85°C). For extreme high-heat requirements, engineering-grade resins like Polycarbonate (Tg 147°C) are required. Selecting the appropriate thermal profile is critical to preventing part failure in end-use environments.


