Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) is a cornerstone of regenerative aesthetics, fundamentally shifting the paradigm from simple volume addition to sophisticated tissue restoration. This biocompatible polymer works by engaging the body’s intrinsic processes, actively stimulating endogenous collagen production. Unlike materials offering temporary correction, PLLA facilitates gradual, sustained regeneration within the dermis over time.
Sourced from renewable resources like corn or sugarcane, PLLA is recognized as a highly sustainable and eco-friendly option. It is a biodegradable polymer that safely metabolizes into water and carbon dioxide. Our expertise lies in ensuring the high molecular weight consistency and verifiable purity of the PLLA we provide—qualities essential for precision medical device manufacturing.
PLLA’s mechanism is potent: it polarizes macrophages, subsequently activating local fibroblasts. This cascade significantly boosts the production of essential extracellular matrix components, yielding demonstrable improvements in skin firmness and texture. Backed by FDA approval and a history of successful applications from facial restoration to body contouring, PLLA is the reliable foundation for products that deliver long-term, natural results.

Production pathway from raw lactic acid to medical-grade PLLA polymer
PLLA Synthesis and Structural Control: The Key to Biostimulation
The biostimulatory potential of PLLA is directly realized through its precise synthesis. The primary method utilized is the ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of lactide dimers. This superior process allows for meticulous control over the final molecular weight (Mw), stereochemistry, and polydispersity index (PDI)—factors directly correlating with a material’s performance consistency and predictable degradation profile.
Structural control remains non-negotiable for predictable biostimulation. Key material characteristics we rigorously manage during synthesis include:
Stereochemical Purity
Maximizing the content of the L-isomer is crucial. This not only enhances the mechanical strength of the final product but, more importantly, ensures controlled, sustained hydrolysis in vivo, releasing only natural L-lactic acid for metabolic clearance.
Crystallinity Optimization
Precise control over polymer chain arrangement is used to tune the material’s degradation kinetics.
Particle Morphology Control
Ensuring uniform particle size (e.g., 20 – 100 μm) and shape is critical to maximize targeted fibroblast activation and mitigate the risk of adverse events like granuloma formation.
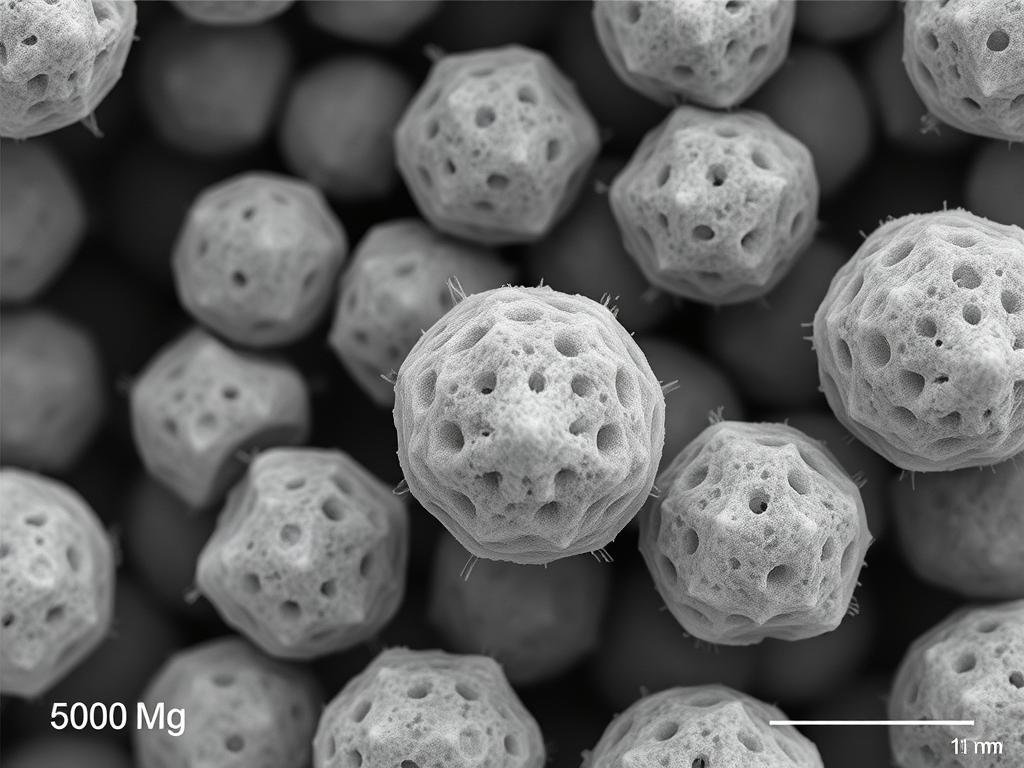

SEM visualization of PLLA microspheres showing surface characteristics critical for cellular interaction
This high degree of structural fidelity translates into products with significantly reduced batch-to-batch variability and highly predictable patient outcomes. Innovations like bismuth-catalyzed ROP are enabling the development of advanced structures, such as stereo-diblock copolymers, for specialized aesthetic and medical applications. Supplying PLLA with ultra-low residual monomer content and guaranteed PDI ensures the safety and efficacy of the final injectable product.
Quality Control (QC) and Regulatory Cluster: Ensuring Medical Safety
The precision achieved during PLLA synthesis must be validated by an exhaustive quality management system. In medical aesthetics, quality is a mandatory condition for patient safety and product efficacy. Our stringent protocols include comprehensive biocompatibility testing adhering to ISO 10993 and USP Class VI, rigorously confirming the absence of adverse reactions in human tissues.
Critical quality metrics are managed through the following rigorous testing framework:
| Quality Parameter | Testing Method | Acceptance Criteria | Efficacy & Regulatory Significance |
| Molecular Weight Distribution | Gel Permeation Chromatography | Mw100,000-300,000 Da with PDI <2.0 | Ensures consistent degradation rate and predictable clinical efficacy. |
| Particle Size Distribution | Laser Diffraction Analysis | 40-63 μm with >90% within range | Critical for injectability, minimized tissue trauma, and uniform tissue response. |
| Residual Monomer Content | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography | <0.1% residual lactide | Prevents cytotoxic risk and unpredictable shifts in degradation kinetics. |
| Endotoxin Levels | Limulus Amebocyte Lysate Test (LAL) | <0.5 EU/mL | Essential for preventing inflammatory and pyrogenic reactions post-injection. |
| Sterility | USP Sterility Tests | No microbial growth detected | Mandatory standard for all injectable biomaterials. |
Regulatory compliance underpins every batch we produce. Our PLLA is developed to be qualitatively and quantitatively equivalent to reference products for FDA submission equivalence, strictly controlling aspects like particle size uniformity and purity. Furthermore, we mandate screening for restricted substances—including color additives under 21 CFR, SVHCs under REACH, and hazardous materials under RoHS. For professionals sourcing materials, this thorough validation translates to mitigated regulatory risk: our PLLA is pre-validated for injectable grades, supporting critical applications in aesthetics, orthopedics, and drug delivery.

Quality control laboratory conducting comprehensive testing of medical-grade PLLA
Raw Material Innovation: Driving Future Products
Innovation in PLLA raw material science is continually pushing the boundaries of regenerative aesthetics. These advancements are expanding PLLA applications far beyond traditional facial volume restoration, enabling sophisticated solutions in targeted tissue engineering and hybrid product development.
Composite PLLA Systems
Hybrid formulations combine PLLA with complementary biomaterials like calcium hydroxyapatite or hyaluronic acid. These systems capitalize on the immediate volumizing effects of traditional fillers alongside the sustained, long-term collagen stimulation of PLLA. Success in this field relies on PLLA grades optimized for superior miscibility and uniform dispersibility with other excipients.
Surface-Modified PLLA
Chemical and physical modifications to the PLLA particle surface are designed to precisely tune cellular interactions and modulate local inflammatory responses. Techniques such as functional group conjugation allow for enhanced biological responses and reduced adverse events. Achieving this level of precision requires PLLA with extremely tight particle size distribution and high batch consistency from the raw material supplier.
Bioactive PLLA Carriers
PLLA microspheres are now functioning as advanced delivery vehicles for crucial bioactive molecules, including growth factors or therapeutic peptides. This approach elevates PLLA from a passive scaffold to an active delivery system, accelerating tissue regeneration through controlled, localized release of these compounds.
Sustainability initiatives are fundamentally reshaping PLLA sourcing. Utilizing advanced bio-based production methods that leverage agricultural waste streams for lactic acid fermentation significantly reduces the environmental footprint of PLLA manufacturing. This commitment to eco-conscious sourcing meets the growing global demand for environmentally responsible, medical-grade materials without compromising quality standards.

Sustainable production pathway for medical-grade PLLA from renewable resources
Supply Chain and Global Sourcing
The efficacy and safety of PLLA products are fundamentally reliant on the integrity of the supply chain, a complex system encompassing specialized manufacturing stages. Understanding this vertical ecosystem is essential for manufacturers and practitioners seeking reliable, high-quality PLLA materials.
Global supply chain network for medical-grade PLLA production and distribution
The foundation of the PLLA supply chain rests on raw material sourcing. Pharmaceutical-grade lactic acid, typically produced through the fermentation of carbohydrate sources, must adhere to exceptionally stringent purity and optical purity requirements. We emphasize rigorous up-stream supplier auditing to guarantee the consistent quality of this foundational component, as its geographical origin and manufacturing process directly influence final polymer performance and regulatory acceptance.
Manufacturing PLLA requires specialized expertise. Production facilities for medical-grade PLLA necessitate state-of-the-art equipment and ISO-compliant cleanroom environments. These sites are concentrated in regions known for advanced biomedical expertise, such as South Korea, Western Europe, and North America. The technical capabilities and quality systems implemented at these locations are critical determinants of final product consistency.

ISO-certified cleanroom facility for medical-grade PLLA manufacturing
Quality assurance extends beyond the plant. Robust traceability systems are non-negotiable, allowing every batch of PLLA to be tracked from its source material through manufacturing and distribution. This detailed documentation provides vital evidence for both regulatory compliance and adverse event investigation. Ultimately, transparent sourcing and comprehensive documentation are not just compliance requirements; they are the necessary standard for ensuring patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Conclusion: Partnership in Regeneration
The efficacy of a regenerative aesthetic product is not created in the clinic, but in the reactor. For manufacturers and compounding professionals, the selection of PLLA is not a generic commodity purchase—it is a strategic decision defined by verifiable purity, precise molecular weight control, and rigorous batch-to-batch consistency.
By prioritizing high-fidelity raw materials, manufacturers mitigate the risk of adverse events and ensure predictable, long-term tissue restoration. In the era of regenerative medicine, material science is the ultimate foundation of patient safety.
Collaborative approach between practitioners and patients for optimal PLLA treatment outcomes
For professionals developing next-generation injectable products, comprehensive knowledge of the PLLA material—including its precise synthesis, validated quality control parameters, and complex biological profile—is critical for market leadership. This expertise empowers manufacturers to deliver consistent, predictable clinical performance.
To achieve sustained excellence in the fast-evolving field of regenerative aesthetics, the integrity of the raw material supply chain is paramount. We invite you to partner with us to secure PLLA materials defined by verifiable purity, structural control, and unwavering regulatory compliance, ensuring your products set the highest standard for safety and efficacy.
Secure the Foundation for Regenerative Excellence
Leverage our polymer science expertise and stringent quality protocols. Contact our Technical Sales Team to discuss your injectable-grade PLLA needs.
FAQs
How is PLLA different from other fillers?
PLLA is an injectable biostimulator, fundamentally different from conventional fillers like HA or CaHA which offer immediate physical volume. PLLA triggers the body’s own controlled response, leading to the synthesis of new, autologous collagen. This unique mechanism creates results that are gradual and naturally sustained, typically persisting for 18-24 months, significantly longer than most passive fillers. The success of this biostimulation hinges on the purity and particle uniformity of the PLLA raw material.
What does PLLA do for skin?
PLLA initiates a controlled, localized inflammatory reaction that stimulates fibroblast activity in the deep dermis. These activated cells synthesize new Type I and Type III collagen fibers and other extracellular matrix components. This process, known as neocollagenesis, improves skin thickness, elasticity, and overall structural support. The material thereby enhances dermal architecture globally, leading to subtle, natural-appearing improvements in firmness and radiance, beyond simple wrinkle reduction.
How long does PLLA filler last?
The clinical effects of PLLA typically persist for 18-24 months, far exceeding the duration of most conventional fillers. This extended longevity is attributed to the durable autologous collagen framework that remains long after the PLLA polymer has safely degraded. The duration is influenced by factors such as:
- The total volume and quality of PLLA administered.
- The number of completed treatment sessions.
- Patient metabolic factors.
- Post-treatment care.
Maintenance treatments every 18-24 months can sustain these regenerative results.
Poly-L-lactic acid side effects
PLLA has a well-established safety profile when used correctly. Common expected reactions include transient erythema, bruising, or edema (usually resolving within one week). Less common adverse events include papules and nodules.
The substantial reduction in nodule risk today is a direct result of advancements in both clinical protocols and raw material quality. For manufacturers, ensuring the batch-to-batch consistency of PLLA raw material—specifically its tight particle size distribution and low residual monomer content—is the fundamental control measure for minimizing these adverse events in the final product.



